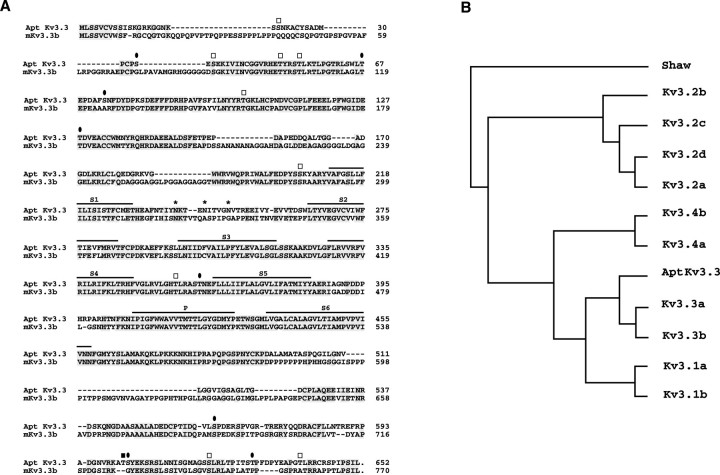
Fig. 2.
Molecular characterization of AptKv3.3.A, Alignment of predicted amino acid sequence of AptKv3.3 with that of the murine splice isoform mKv3.3b. The six transmembrane domains (S1–S6) and the pore domain (P) are indicated above the sequence. Also indicated are consensus sites for N-linked glycosylation (asterisks) and phosphorylation by protein kinase C (open squares), protein kinase A (filled square), and calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase (filled ovals). Amino acid identities areshaded. B, Phylogenetic comparison of AptKv3.3 to members of the mammalian Kv3 family. The sequences used for comparison included splice isoforms of each Kv3 subtype and, with the exception of murine Kv3.3a and Kv3.3b, were from rat (see Materials and Methods). The phylogenetic tree demonstrates that AptKv3.3 is most related to mammalian Kv3.3. Analysis by the parsimony method was performed using the PROTPARS program in the Phylogeny Inference Package (PHYLIP) (Felsenstein, 1989). In this algorithm, the DrosophilaShaw K+ channel was used as the outgroup.