Fig. 4.
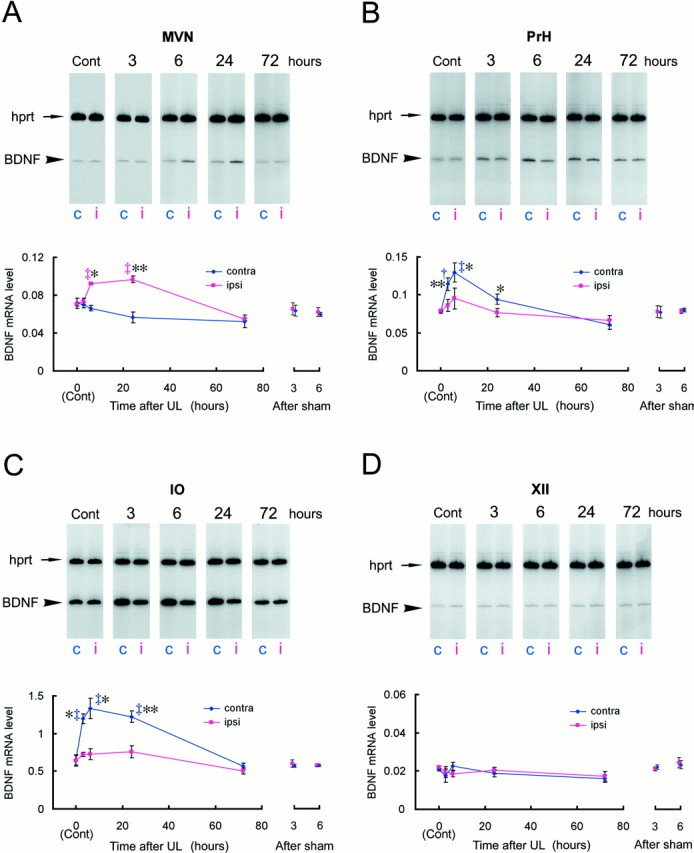
BDNF mRNA induction during the early phase of vestibular compensation. The BDNF mRNA expression levels were evaluated by RT-PCR coamplification in the MVN (A), PrH (B), IO (C), and XII (D), at 3, 6, 24, and 72 hr after UL. The BDNF mRNA levels were defined as amounts of RT-PCR products of BDNF normalized by those of the internal standardhprt gene, which was coamplified with BDNF in the same reaction tube. Each data point in the graphs represents the mean of the BDNF mRNA levels in a total of 18 rats in triplicate experiments (n = 6 rats per experiment). Representative gel patterns are shown at the top of each graph. c, Contralateral; i, ipsilateral. For the MVN (A), a mixed-design two-way ANOVA revealed significant effects of survival time (p < 0.005), laterality (p < 0.0001), and interaction of survival time and laterality (p < 0.0001). The ANOVA also showed significant effects for the PrH (B): survival time (p = 0.011), laterality (p < 0.0001), and interaction (p < 0.0001). Similarly, the ANOVA for the IO (C) indicated significant effects of survival time (p < 0.001), laterality (p < 0.0001), as well as interaction (p < 0.0005). Daggersrepresent statistical significance compared with control expression levels determined by Duncan's post hoc multiple comparison (†p < 0.05; ‡p < 0.01). Asterisksdenote a significant difference in BDNF mRNA levels between ipsilateral and contralateral sides revealed by a post hoc pairedt test (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01). The ANOVA indicated that there were no significant effects on time, laterality, and interaction for the control nucleus, XII (D). The BDNF mRNA levels in the sham-operated animals at 3 and 6 hr were also presented on theright side of each graph.
