Fig. 2.
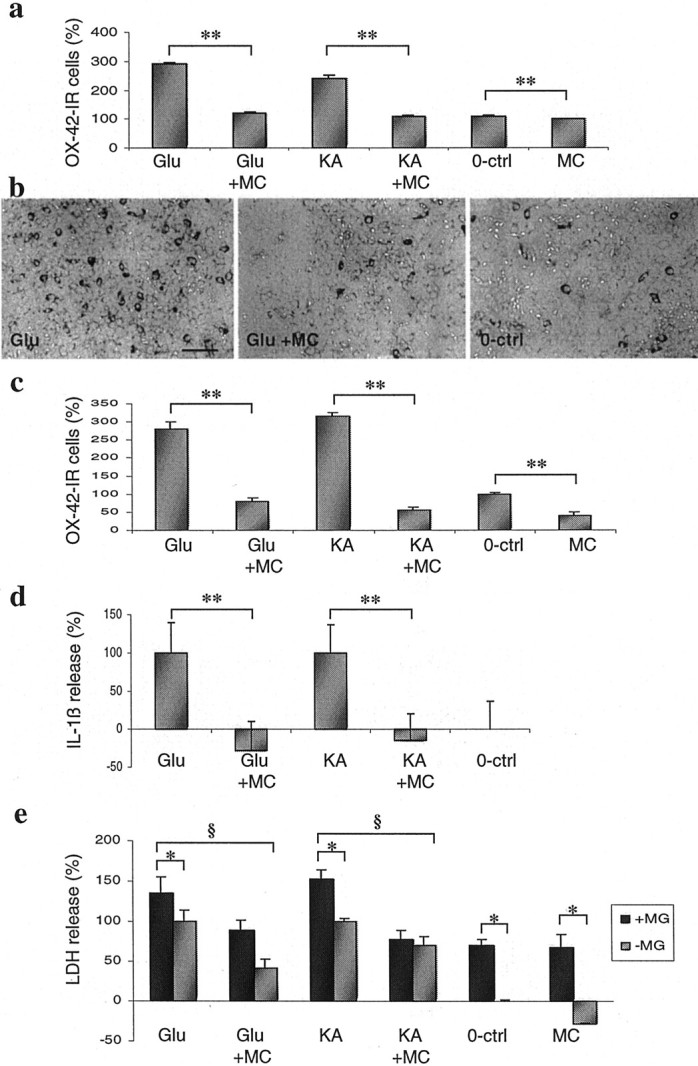
Minocycline (MC) inhibits excitotoxin-induced proliferation of microglial cells independently of neuronal cell death. a, In SC cultures, the number of OX-42-immunoreactive (OX-42-IR) microglial cells is significantly increased after a 24 hr exposure to 500 μmglutamate (Glu) and 100 μm kainate (KA). Minocycline (0.02 μm) treatment completely prevents the microglia proliferation and decreases the microglia cell number even in unexposed control cultures (0-ctrl). Data are presented as the mean ± SD counted in a blind manner and pooled from two independent experiments (n = 8). **p < 0.01; single-factor ANOVA. b, Representative photomicrographs of the effect of glutamate and minocycline on OX-42-immunoreactive cells. Scale bar, 250 μm. c, A 24 hr exposure of neuron-free glial cultures to 500 μmglutamate and 500 μm kainate results in microglia proliferation, which is inhibited by 0.2 μm minocycline treatment. Minocycline also inhibits the spontaneous microglia proliferation. Data are presented as the mean ± SD counted in a blind manner (n = 3). **p < 0.05; single-factor ANOVA. d, Exposure of SC cultures to excitotoxins causes increased IL-1β release, which is reduced by minocycline treatment. The exposure and treatment of these cultures were done as described in Figure 1a. Data are presented as the mean ± SD pooled from two independent experiments (n = 6). **p < 0.01; single-factor ANOVA. e, Increased number of microglia in SC cell cultures enhances the excitotoxicity, which was inhibited by minocycline. Adding microglia onto SC cell cultures (+MG), excitotoxicity of 500 μm glutamate and 100 μm kainate is increased significantly (*p < 0.05; single-factor ANOVA) when compared with the normal mixed SC culture (−MG). The basal LDH release is also enhanced significantly (*p < 0.05; single-factor ANOVA) in microglia-rich cultures. Minocycline (0.02 μm) treatment 30 min before excitotoxin exposures was able to provide significant (§p < 0.05; single-factor ANOVA) neuroprotection. Data were presented as the mean ± SD pooled from two independent experiments (n = 6).
