Fig. 12.
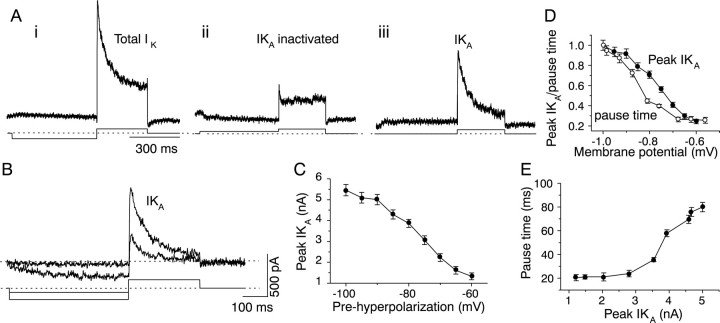
IK(A) in pause–build neurons. K+ currents were recorded in saline containing 2 μm TTX. A, Isolation ofIK(A). i, Bottom trace, The voltage-clamp protocol used to test for the presence of IK(A). The cell was held at −60 mV and then prehyperpolarized to −100 mV for 500 msec, followed by a depolarization to −10 mV for 300 msec to evoke K+efflux and then returned to its holding potential. Top trace, K+ current evoked by this protocol. There was no measurable K+ current during the prehyperpolarizing step in this cell. ii, Bottom trace, Protocol used to inactivateIK(A). The cell was held at −60 mV, predepolarized to −30 mV for 500 msec, followed by a depolarization to −10 mV, and then returned to its resting potential. Top trace, K+ current during the 300 msec depolarization to −10 mV. iii, The K+ current remaining after subtraction ofii from i shows the time course and magnitude of IK(A) evoked during the voltage step to −10 mV. B, IK(A)evoked by prehyperpolarizations of two different magnitudes; the larger prehyperpolarization evokes the largerIK(A). Current traces shown are the subtracted traces resulting from a similar protocol to the one used inA, except that the prehyperpolarization was varied. In this cell, a small inward current is triggered by the larger hyperpolarizing step. C,IK(A) has a monotonic dependence on the magnitude of the prehyperpolarization. D, Similar variation of pause time and IK(A) with the magnitude of prehyperpolarization. E, Variation of pause time with peak IK(A) amplitude. Data inC–E are the mean ± SEM of the same 11 cells.