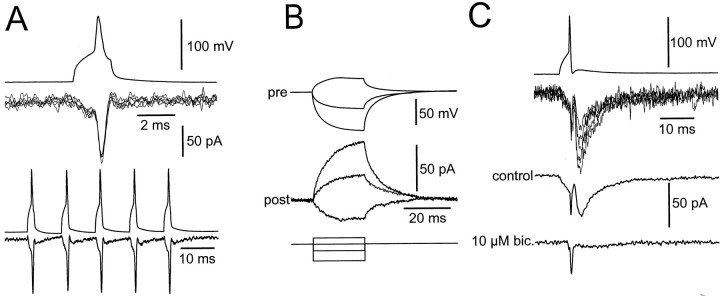
Fig. 6.
Electrical coupling in a subset of BC–BC pairs. A, Top panel, Electrical PSCs evoked by single presynaptic action potentials in a tentatively identified BC–BC pair. Presynaptic action potential is shown attop; single electrical PSCs are shown atbottom; six sweeps are superimposed. A,Bottom panel, Electrical PSCs evoked by a train of five presynaptic action potentials evoked with a frequency of 100 Hz (average from 15 sweeps). Note that the amplitude of the electrical PSCs is approximately constant and that the electrical PSCs are mirror images of the presynaptic action potentials. B, Postsynaptic voltage changes evoked by long depolarizing and hyperpolarizing current pulses (0.4, −0.4, and −1 nA) applied to the presynaptic interneuron. Presynaptic voltage (top), corresponding postsynaptic current (center), and pulse protocol (bottom) are depicted. Note that the current–response in the postsynaptic cell is an approximate mirror image of the voltage change in the presynaptic neuron. Same pair as in A is shown. C, Combined electrical and chemical transmission in another tentatively identified BC–BC pair. Presynaptic action potential (top), single electrical and chemical PSC traces (5 sweeps superimposed), average (from 15 sweeps), and average in the presence of 10 μm bicuculline methiodide (from 25 sweeps;bottom) are illustrated.