Fig. 8.
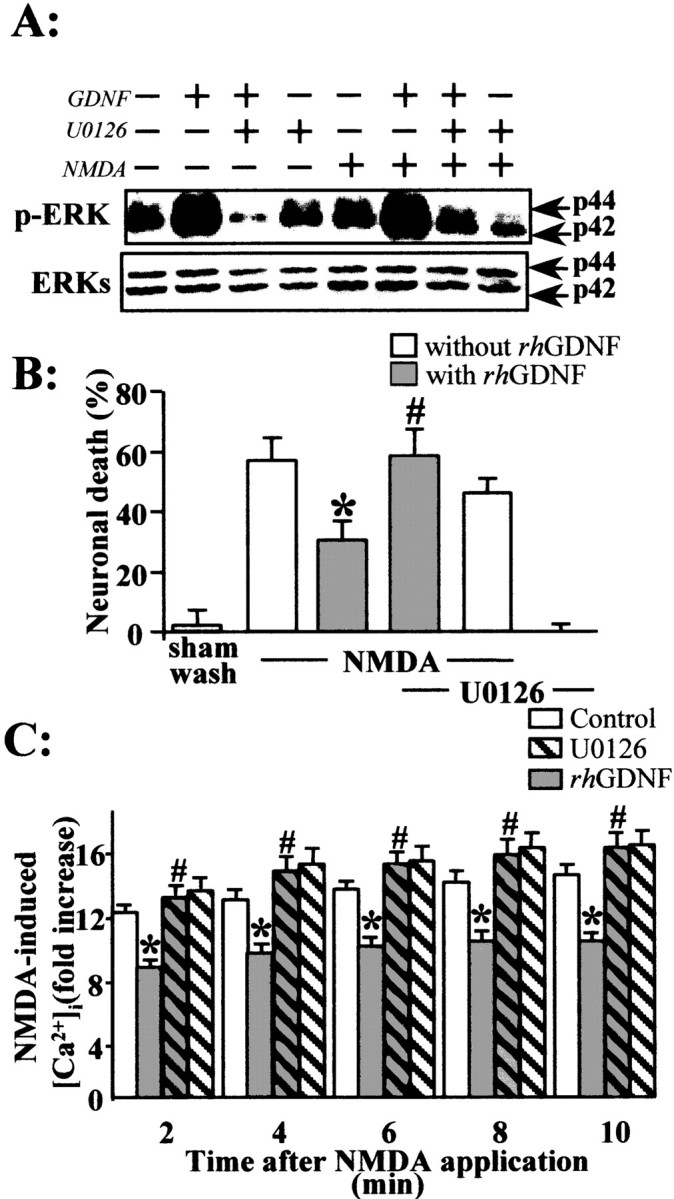
The MEK kinase inhibitor U0126 blocks the rhGDNF-induced reduction of NMDA-evoked calcium influx.A, Mouse primary cortical neurons were treated for 15 min with rhGDNF (10 ng/ml) in the presence of U0126 (1 μm) and with or without NMDA (12.5 μm). Aliquots of whole-cell lysates were separated by SDS-PAGE, transferred to membranes, and incubated with the anti-MAPK antibody (p-ERKs, ERKs). Representative immunoblots are shown, demonstrating the specific blockade of ERKs phosphorylation by U0126 treatment. B, Neuronal death percentage was estimated by LDH release (mean ± SEM;n = 12) after a 24 hr exposure to NMDA (12.5 μm) in mixed neuron–glia cortical cultures in the presence (gray bars) or absence (white bars) of rhGDNF and treated or not treated with 1 μm U0126. * indicates significantly different from NMDA alone; # indicates significantly different from NMDA plus GDNF by ANOVA, followed by Bonferroni–Dunn's test (p < 0.05). C, Calcium imaging was performed as described in the legend to Figure 7. Neurons (13–14 DIV) were exposed to serum-free medium for 45 min in the absence (control; vehicle treated; white bars) or presence (gray bars) of rhGDNF (10 ng/ml) and with (hatched bars) or without (unhatched bars) U0126 (1 μm). Time course of the effect of rhGDNF on the NMDA-induced [Ca2+] increase, with or without treatment with 1 μm of U0126. Data are expressed as an NMDA-induced fold [Ca2+]i. Results represent the mean ± SEM of three separate preparations (3 coverslips; 20 neurons being imaged per coverslip in a single microscopic field). * indicates significantly different from NMDA; # indicates significantly different from NMDA plus GDNF by ANOVA for repeated measures followed by a Bonferroni–Dunn's test for multiple comparisons (p < 0.05).
