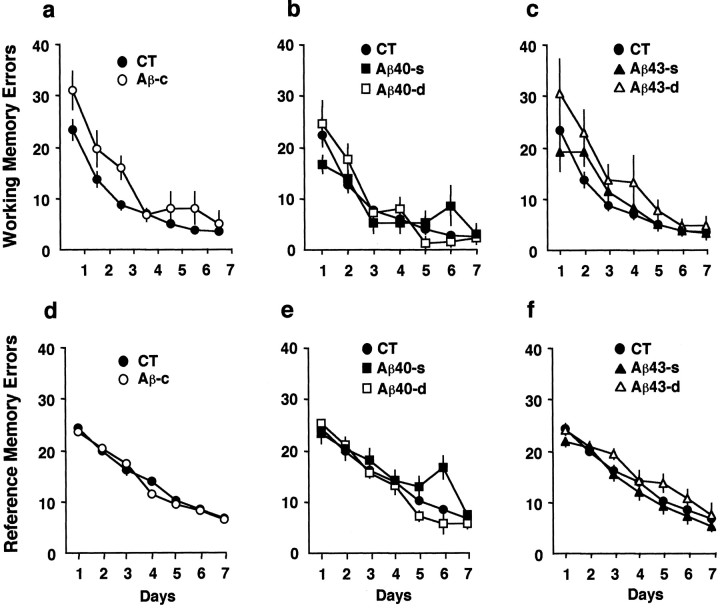
Fig. 1.
Spatial learning on the radial arm maze, 4 weeks after focal injections of amyloid peptides, shows the ability of rats to learn the working memory element (a–c) or the reference memory element (d–f).a, Rats injected with combined fragments (Aβ-c) showed impairment in the working memory aspect in the first few days of training (blocks of 8 trials/d) compared with control rats (CT). This difference was modest but significant. b, Rats injected with either dose of Aβ40 [single dose (Aβ40-s); double dose (Aβ40-d)] were not significantly impaired in working memory. c, Whereas rats injected with the low dose of Aβ43 were not impaired in learning, those rats injected with the high dose of Aβ43 showed an overall impairment. d–f, All rats were able to learn the reference memory aspect of the task to the same level as the control rats. The y-axis denotes the total number of reentries made in the working memory element (a–c) and entries into nonbaited arms in the reference memory element (d–f) of the task.