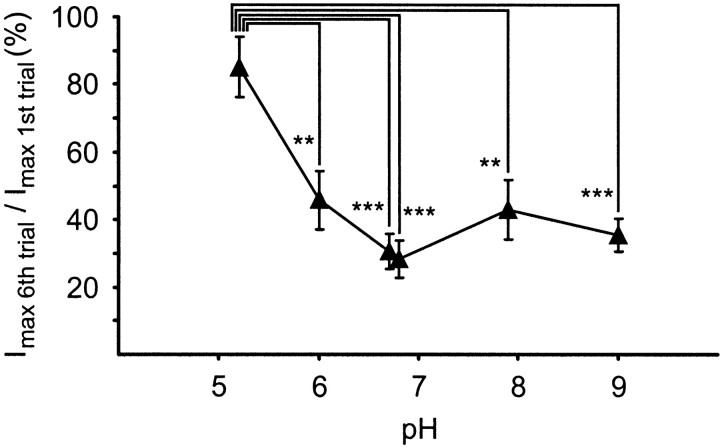
Fig. 8.
Effects of various bath pH values on desensitization in isolated RPeD1 neurons. Isolated RPeD1 neurons were exposed to series of six FMRFamide pulses (pipette concentration, 0.1 mm, 1 sec) at 15 sec intervals, and the induced inward currents were measured under TEVC (holding potential, −100 mV) in bath media buffered at pH 5.2, 6.0, and 6.7 (MES-buffered), 6.8 and 7.9 (HEPES-buffered), and pH 9.0 (Tris-buffered). The amplitude of the sixth response in each series was expressed as a percentage of the first response, and the mean values for each experiment were plotted against the pH. A statistical analysis revealed that acidification of the bath medium to pH 5.2 significantly reduced desensitization of the FMRFamide-induced inward current compared with all other pH values tested (ANOVA: F(5,29) = 8.684,p < 0.001, followed by post hocTukey HSD tests for pairwise comparison; p ≤ 0.01 for all pairs; **p ≤ 0.01, ***p ≤ 0.001). These tests also showed that none of the differences between the desensitization levels at pH 6.0, 6.7, 6.8, 7.9, and 9.0 were significant (Tukey HSD tests; p values > 0.5).