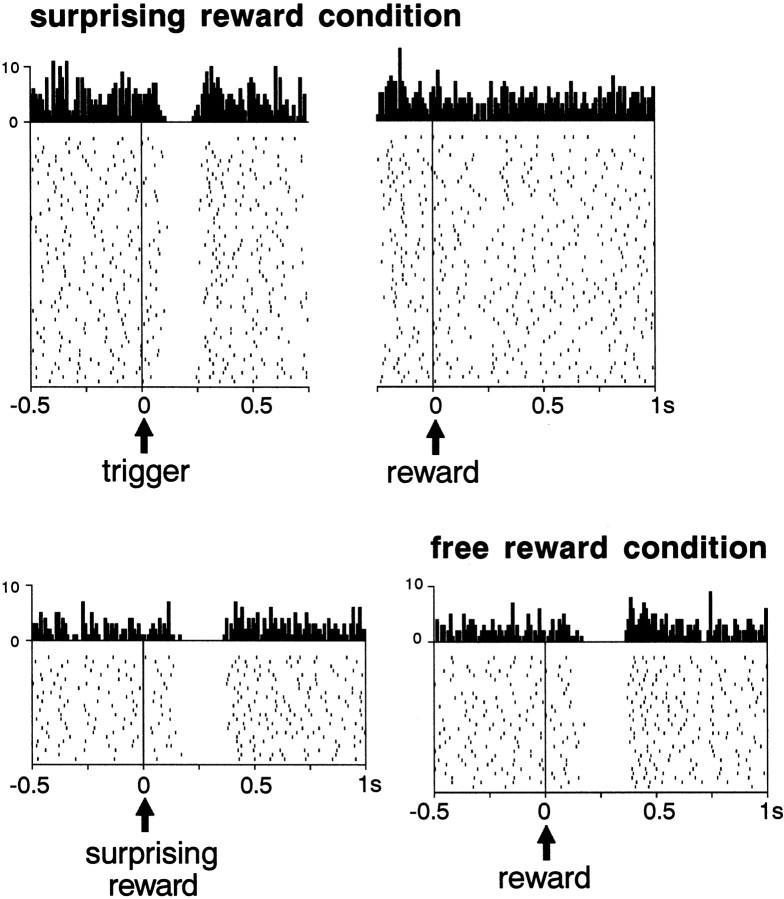
Fig. 6.
Influence of delivering reward unexpectedly early in the instrumental task condition in one tonically active neuron. Same conventions as in Figure 3. Data were collected during the same test session in which reward was delivered normally after target reaching (usual trials) or unexpectedly soon at the beginning of a trial (surprising trials). The two types of trials occurred pseudorandomly within the same block of trials and were separated off-line for analysis. The raster and histogram display in the lowerrightpanel is for a separate block of trials in which the liquid was given outside of the task at unpredictable intervals (free reward condition). This neuron responded in a similar way to reward, both in the surprising and free reward trials.