Fig. 1.
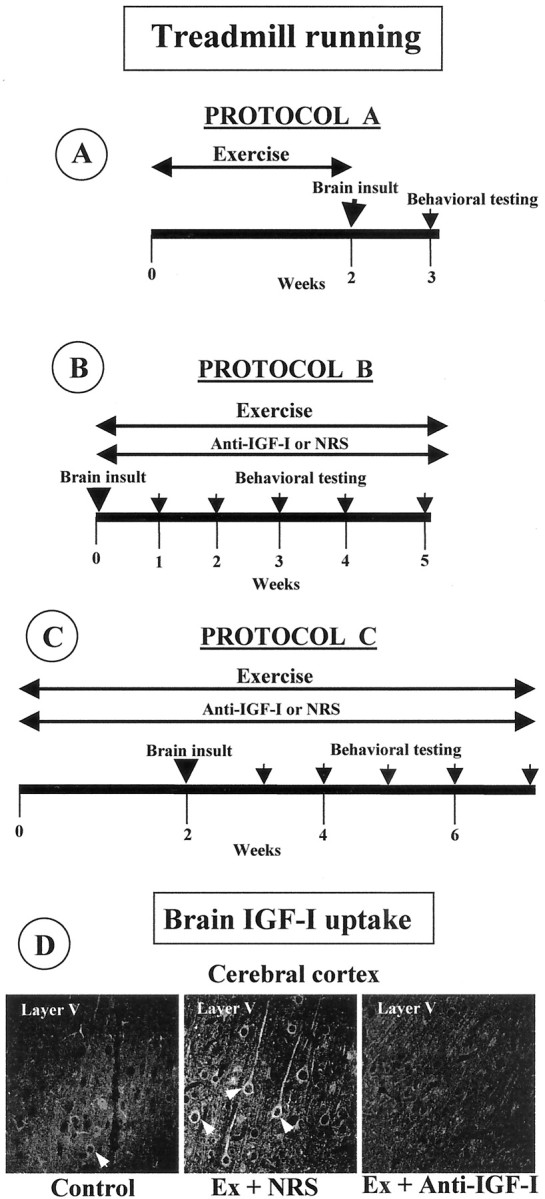
A–C, Treadmill running and anti-IGF-I delivery schedules. A, Protocol A: exercise before brain insult. Animals run during 15 d before brain insult (3AP in rats and domoic acid in mice). Behavioral testing was conducted 5–7 d later. B, Protocol B: exercise after brain insult. Brain-damaged animals ran for 4–5 weeks and were evaluated in the rotarod once per week (pcd mice and 3AP-injected rats).C, Protocol C: animals exercised both before and after brain insult (3AP). Behavioral testing was also done every week. In a parallel series of experiments, an anti-IGF-I infusion was delivered in protocols B and C to exercising animals. Control exercising animals received an NRS infusion. In all protocols, animals were killed for anatomical evaluation after the last behavioral evaluation.D, IGF-I antiserum inhibits exercise-induced brain accumulation. Control, Sedentary animals show negligible IGF-I immunostaining in the brain, whereas exercised animals receiving NRS (Ex + NRS) show a marked increase that is inhibited when an anti-IGF-I infusion is administered simultaneously (Ex + Anti-IGF-I). A representative brain area is shown.
