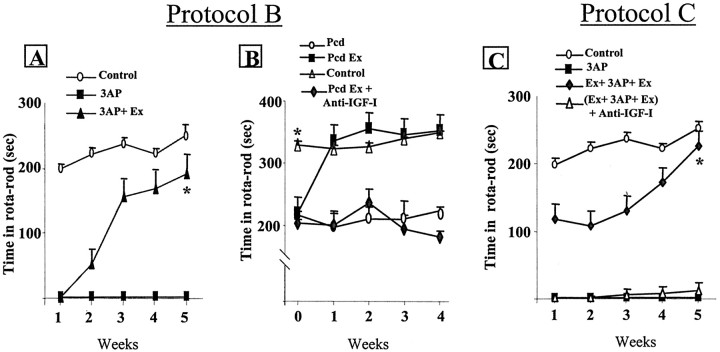
Fig. 3.
Exercise induces recovery of behavioral performance in ongoing neurodegeneration. A, Rats submitted to treadmill running after 3AP insult gradually recover motor coordination and reach normal performance after 5 weeks of running (*p < 0.002 vs 3AP). B, pcd mice with moderate, albeit significantly impaired motor coordination underwent exercise training and recovered normal motor performance within 1 week. They kept normal motor coordination for the duration of the study, whereas sedentary pcd mice remained ataxic. However, exercising pcd mice simultaneously receiving an anti-IGF-I infusion did not recover limb coordination (*p < 0.001).C, Rats were submitted both before and after 3AP insult to treadmill running with simultaneous infusion of NRS and recovered full motor coordination after 5 weeks. However, rats receiving simultaneously an anti-IGF-I infusion remained severely impaired [*p < 0.01 vs 3AP and (Ex + 3AP + Ex) + Anti-IGF-I].