Fig. 2.
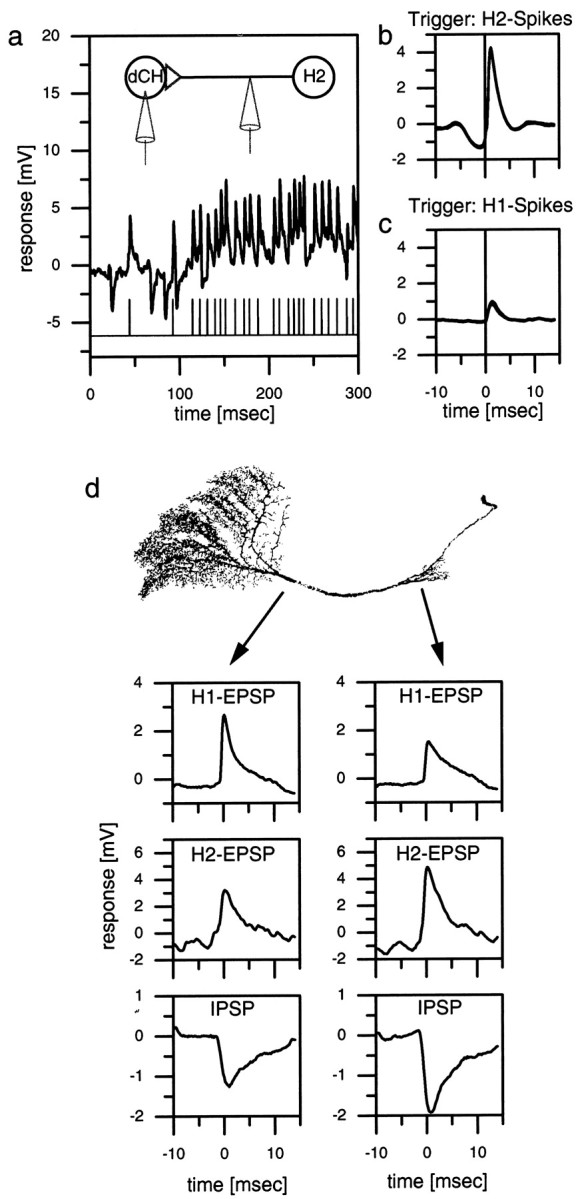
a–c, Double recording of an H1 or an H2 cell and a dCH cell. a, Singletrace of an intracellular dCH cell recording and an extracellular H2 recording. Each extracellular recorded spike in the H2 elicits an large-amplitude EPSP in the dCH cell.b, H2 spike-triggered average of the dCH cell signal. The peak of the EPSP occurs ∼1 msec after the spike of the H2 (vertical line). c, H1 spike-triggered average of the dCH cell signal. The amplitude of the averaged EPSP is only one-third that of the H2-triggered EPSP.d, Dual electrode intracellular recording from a dCH cell. The location of the recording electrodes indicated by the origin of the arrows on a reconstructed dCH cell is shown.Left plots, The averaged H1 EPSPs (top), H2 EPSPs (middle), and IPSPs (bottom) of the lobula plate electrode. Right plots, The respective signals of the protocerebral electrode. In the dendritic recording, the amplitude of H1 EPSPs is larger than that of the protocerebral recording. H2 EPSPs and IPSPs are larger in the protocerebral recording. Similar data have been obtained in three additional preparations (dCH, n = 2; vCH,n = 1).
