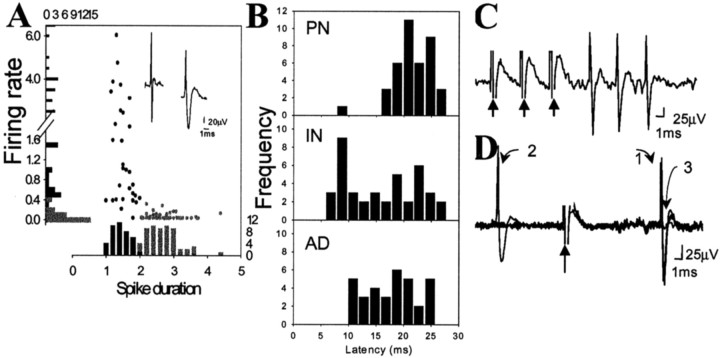
Fig. 2.
Characteristics of BLA neuronal activity. A, Evoked spikes were characterized as originating from projection neurons or interneurons using the criteria of firing rate and spike duration. Aligned with they-axis is a distribution histogram of firing rates, and aligned with the x-axis is a distribution histogram of spike durations (from a randomly selected sample of neurons,n = 59). The circles represent each individual neuron plotting its spike duration as a function of its firing rate. The presumed interneurons (black circles) consistently show faster firing rate and shorter spike duration than do the presumed projection neurons (gray circles).B, Antidromic responses of BLA neurons that project to the mPFC (AD; n = 34) display longer latencies than mPFC-evoked responses in BLA interneurons (IN; n = 40). Therefore, the significantly shorter latency of mPFC-evoked responses on BLA interneurons compared with projection neurons (PN;n = 42) cannot be attributable to antidromic activation of a BLA neuron that projects to the mPFC. Antidromic activation of BLA projection neurons is confirmed by the ability of the spikes to follow high-frequency stimulation (300 Hz, 0.6 mA, 0.4 msec duration, three stimuli at arrows) (C) and constant response latency (1), and collision (3) with a spontaneous spike (2) (D).