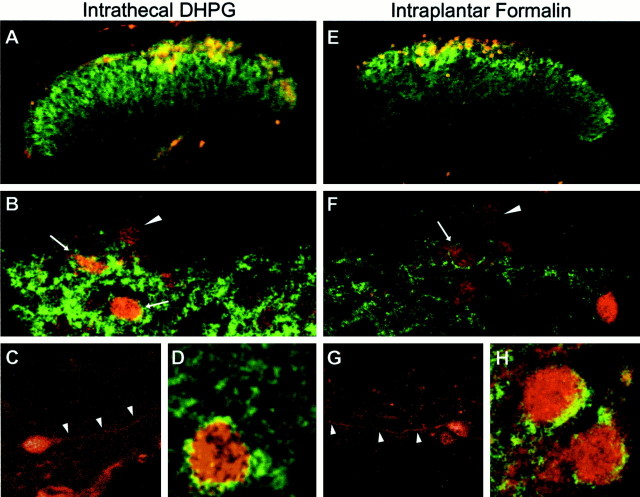
Fig. 6.
Colocalization of phospho-ERK and mGluR5 in mouse dorsal horn after intrathecal DHPG (10 nmol) (A–D) or intraplantar formalin injection (E–H). A, E, Fluorescence images showing the distribution of mGluR5 (green) and phospho-ERK (red) immunoreactivity in the lumbar spinal cord dorsal horn 5 min after DHPG (A) or 8 min after 2% subcutaneous injection of formalin in the right hindpaw (E).B and F show higher-power examples of confocal images showing the distribution of mGluR5 (green) in relation to phospho-ERK (red) in the dorsal horn. Note that some phospho-ERK cells also have apparent membrane labeling for mGluR5 (arrows), whereas other phospho-ERK-positive cells contain no detectable mGluR5 (arrowheads).C and G show higher magnifications of phospho-ERK staining of dorsal horn neurons. Note the labeling of dendritic processes (arrowheads), which are typically seen when cells are observed using a confocal microscope.D and H show higher magnification of additional example neurons with apparent membrane labeling for mGluR5 and somatic phospho-ERK. These images are representative of similar results obtained from three separate animals.