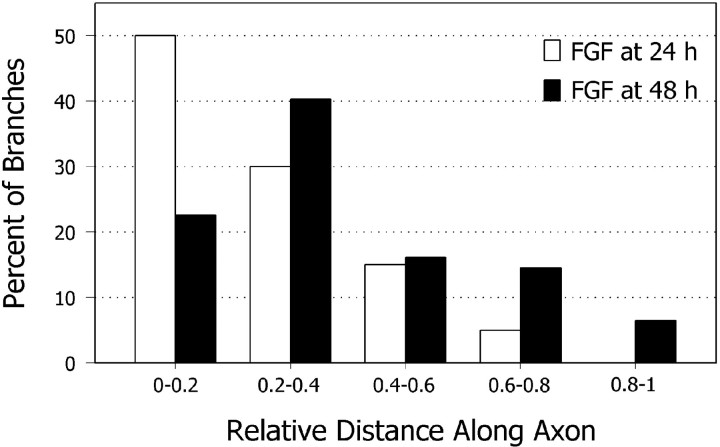
Fig. 5.
FGF-2 induces branches preferentially at distal regions of the axon. Bar graph compares positions of axon branches elicited with FGF-2 added at different stages of development. Spontaneously formed axon branches were scattered evenly along the axon (data not shown). Branches induced by bath application of FGF-2 tended to cluster at regions along the axon corresponding to positions of the primary growth cone at the time when FGF-2 was applied. Distances are given in relative distances from the cell body and do not denote actual axon lengths. The results graphed were obtained from one experiment (n = 40 branches per 43 axons at 24 hr;n = 62 branches per 58 axons at 48 hr), but each experiment was performed three times with similar results. FGF-2 was applied for 2 hr. Branching was assessed at 96 hr after plating.