Fig. 6.
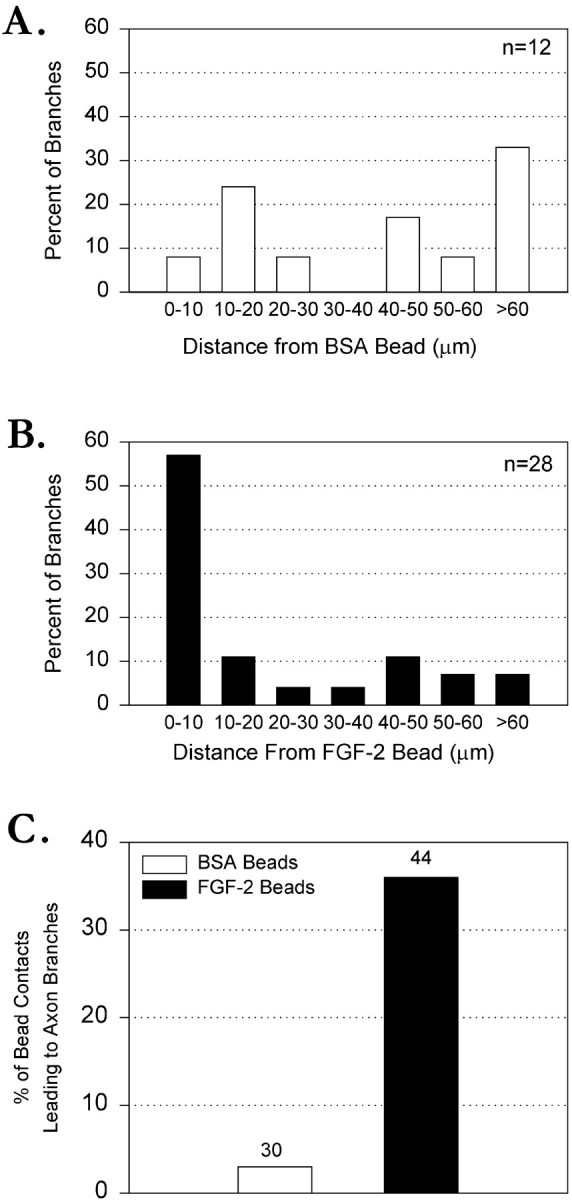
FGF-2-coated beads induce local axon branching. A, Bar graph showing the distribution of branches along axons contacted by BSA beads. n refers to the number of axon branches found at any part of the axons contacted by beads. Note that branches are distributed randomly along the axons.B, Bar graph showing the distribution of branches along axons contacted by FGF-2 beads. n refers to the number of axon branches found at any part of the axons contacted by beads. Note that branches are located preferentially (57%) within 10 μm of an FGF-2 bead but are distributed randomly along the remaining regions of the axons. C, Bar graph comparing the effectiveness of FGF-2 versus BSA beads in promoting branching. Percentages of bead contacts leading to axon branches are calculated for beads only within 10 μm of a branch. For BSA beads, 3% (n = 30) were associated with a branch versus 36% of FGF-2 beads (n = 44).
