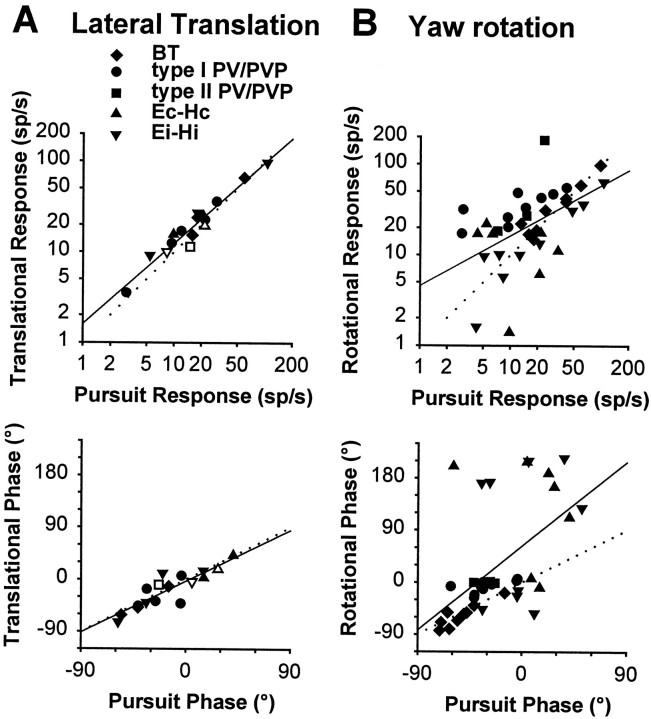
Fig. 8.
Functional distinction between sensory and motor signals during lateral translation (A) and yaw rotation (B). This is illustrated by plotting the peak firing rate (top) and phase (bottom) during movement while an animal fixated a central earth-fixed target versus the corresponding peak firing rate and phase during horizontal smooth pursuit with the animal stationary. The stimuli during translation and rotation were adjusted such that the elicited eye movements were close to identical to those during smooth pursuit (0.5 Hz, ±10°). Different symbols are used for different classes of cells (BT, type I PV/PVP, type II PV/PVP, Ec-Hc, and Ei-Hi).Opensymbols in Acorrespond to the few (3) cells that were tested for both stable gaze and suppression conditions and exhibited small but consistent responses during TrVOR suppression (22–68 spikes · sec−1 · g−1).Dotted lines with unity slope indicate equal responses during head movement and pursuit. Solid lines are linear regressions (A, top, slope = 0.89, R2 = 0.94; A, bottom, slope = 0.98,R2 = 0.77; B, top, slope = 0.55,R2 = 0.28; B, bottom, slope = 1.61,R2 = 0.30). See previous figure legends for abbreviations.