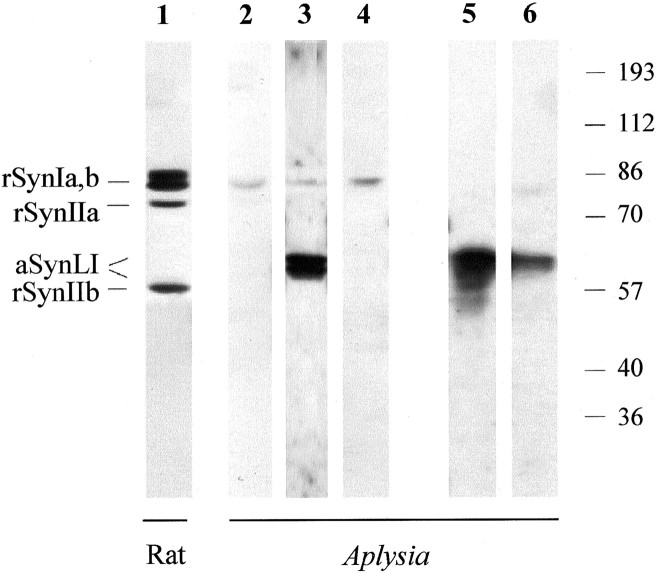
Fig. 1.
Synapsin-like immunoreactivity inAplysia nervous tissue. Proteins from extracts of rat cerebral cortex (5 μg protein, lane 1) andAplysia ganglia (30 μg protein, lanes 2–6) were separated by SDS-PAGE on 9% polyacrylamide gels, transferred to nitrocellulose membranes, and immunoblotted with the following antibodies diluted 1:1000: lanes 1 and3, G423; lane 2, preimmune G423;lane 4, synapsin-preadsorbed G423; lane 5, G177; lane 6, synapsin preadsorbed G177. Immunoreactivity was revealed using the chemiluminescence detection system. Preadsorption of the antibodies markedly decreased or virtually abolished the immunoreactivity in the samples from both rat (data not shown) and Aplysia nervous systems. Molecular mass markers are shown on the right in kilodaltons.rSynIa,b, Rat synapsin Ia/Ib; rSynIIa, rat synapsin IIa; aSynLI, Aplysiasynapsin-like immunoreactivity; rSynIIb, rat synapsin IIb.