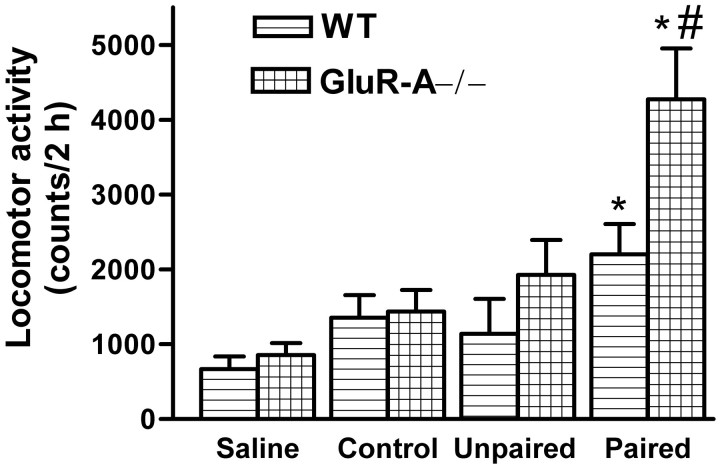
Fig. 7.
The effect of repeated d-amphetamine administration on amphetamine-induced locomotor activity of GluR-A−/− mutant mice and their wild-type (WT) controls. The mice were injected with 2 mg/kg (subcutaneous) amphetamine or 10 ml/kg saline for 5 d in either locomotor activity cages (Paired) or home cages (Unpaired). After 5 d, immediately before being transferred into locomotor activity cages, the saline-treated animals received either saline injection (Saline) or 0.5 mg/kg amphetamine (Control), and the amphetamine-treated animals received 0.5 mg/kg amphetamine. The bars indicate mean ± SEM (n = 12–16) horizontal activity counts for 2 hr sessions. *p < 0.05 for the difference from the corresponding saline and control group; #p < 0.05 for the difference from the corresponding control mouse line; Duncan's test.