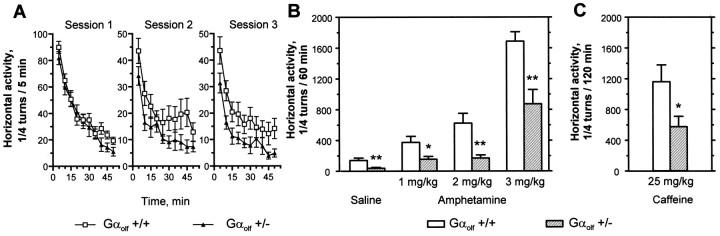
Fig. 6.
Effects of amphetamine and caffeine on the locomotor activity of Gαolf +/− mice. The horizontal activity of male heterozygous (Gαolf +/−) and wild-type (Gαolf +/+) mice was measured in three sessions. In each session, animals were allowed to habituate to the testing apparatus for 50 min and received saline injections in the two first sessions and amphetamine (1, 2, or 3 mg/kg) or caffeine (25 mg/kg) in the third session. A, Spontaneous activity of Gαolf+/− and Gαolf +/+ mice during the 50 min habituation period in the three sessions. Activities were significantly lower in mutant mice during sessions 2 and 3 (two-way ANOVA;F(1,260) = 22.3 andF(1,260) = 33.1, respectively;p < 0.001). B, Effects of amphetamine or saline injections on the locomotor activity of Gαolf +/− mice. Data for saline correspond to the results obtained in the second session. C, Effects of caffeine on the locomotor activity of Gαolf +/− mice. The results are the mean ± SEM of data obtained with 7–14 animals. *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01, significantly different from wild-type controls with the same treatment.