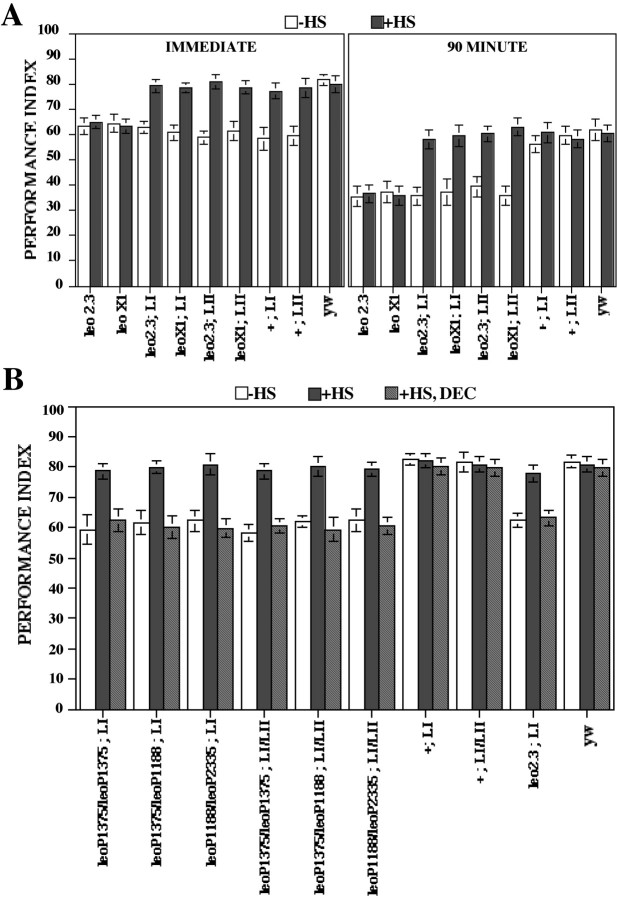
Fig. 5.
Conditional rescue of the learning and memory deficit of leo mutants. A, Conditional rescue of learning and memory deficits of viable alleles. Learning (IMMEDIATE) and 90 min memory was assessed inleo2.3,leoX1,leo2.3;LI,leo2.3;LII,leoX1;LI,leoX1;LII, and control animals (yw). To investigate potential nonspecific effects of the LI and LII transgenes, flies homozygous for the transgenes but not harboring the mutations in leo were used as additional controls. The mean PI ± SEM is shown for each stock. The performance index was calculated as by Skoulakis and Davis (1996). Learning in mutants reared under conditions that silence the transgenes (18°C; hatched bars) was identical to mutants without the transgenes and significantly different compared with control animals. One-way ANOVA showed significant effects of genotype (F(8, 78) = 16.245;p < 0.001). Planned comparisons showed significant differences among yw and the mutants (p < 0.001) but not among yw and +;LI or +;LII controls or amongleo2.3 andleoX1 compared with uninduced (−HS),leo2.3;LI,leo2.3;LII,leoX1;LI, andleoX1;LII. Similarly, one-way ANOVA indicated significant effects of genotype in 90 min memory (F(8, 74) = 14.925;p < 0.001) and was confirmed for mutants compared with yw (p < 0.001). There were no significant differences among yw and +;LI or +;LII strains. However, learning and 90 min memory of the mutants was not significantly different from controls when animals were trained after transgene induction (black bars), indicating full rescue of the learning and memory deficits. n > 8 for all stocks. B, Reversible conditional rescue of learning deficits of lethal homozygotes and heteroallelics. Learning was assessed in the indicated lethal homozygotes and heteroallelics obtained under protocol HS B without previous transgene induction (−HS, white bars) after transgene induction and recovery (+HS, black bars) or after a lengthy recovery period for the levels of LEO to decay (+HS, DEC, hatched bars). The mean PI ± SEM is shown for each stock. One-way ANOVA indicated significant effects of genotype (F(9, 96) = 14.836; p < 0.001), and subsequent planned comparisons verified significant differences among mutants and control (yw) strains (p < 0.001) but not for yw and +;LI or +;LI/LII flies under uninduced conditions (−HS). n > 8. In contrast, ANOVA did not indicate differences among all strains after transgene induction (+HS), indicating complete rescue of the learning deficit. n > 7. However, decay of the induced LEO protein (+HS, DEC) resulted in significant loss of learning in mutant stocks compared with age-matched controls (p < 0.001) but not among yw and +;LI or +;LI/LII strains. Therefore, the amount of LEO present in the head of mutants at the time of conditioning is essential for learning.