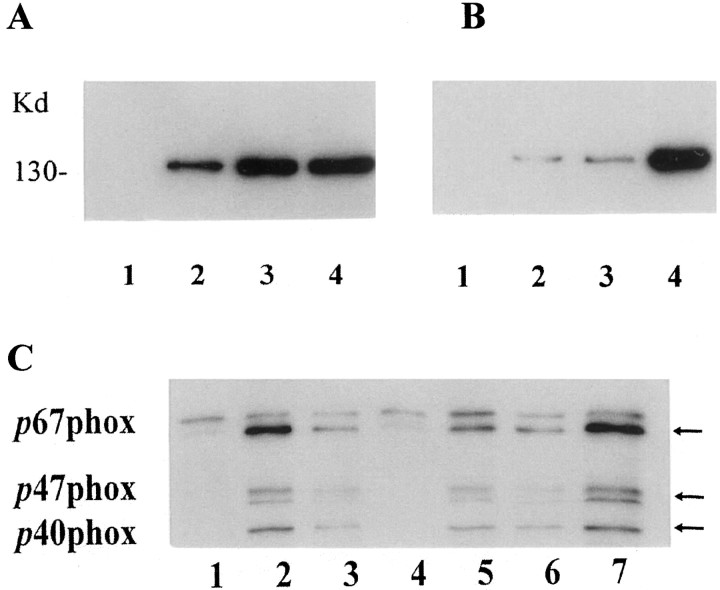
Fig. 3.
iNOS (A, B) and NADPH oxidase (C) induction in activated microglia. A, B, iNOS was detected (A, B) by immunoblot with iNOS antibodies. A, Microglia were incubated with (1) vehicle, (2) high-dose (150 μg/ml) DA-Q-M MES 23.5 cell membranes, (3) high-dose (200 μg) PD IgG, and (4) LPS (4 μg/ml) for 2 d.B, Microglia were incubated with (1) vehicle, (2) low-dose (15 μg/ml) DA-Q-M membranes, (3) low-dose (20 μg/ml) PD IgG, and (4) low-dose DA-Q-M membranes plus IgG. Note that increased iNOS in microglia after treatment with DA-Q-M membranes, IgG and LPS, and a synergetic effect of DA-Q-M membranes + IgG on microglia iNOS.C, NADPH oxidase was detected by three antibodies (p67phox, p47phox, and p40phox) in microglia treated with (1) vehicle, (2) high-dose PD IgG, (3) high-dose DA-Q-M membranes, (4) trypsin-treated DA-Q-M membranes, (5) low-dose PD IgG, (6) low-dose DA-Q-M membranes, and (7) low-dose DA-Q-M membranes + PD IgG. Arrows indicate three isoforms of NADPH oxidase reacting with antibodies ofp67phox, p47phox, andp40phox, respectively.