Fig. 8.
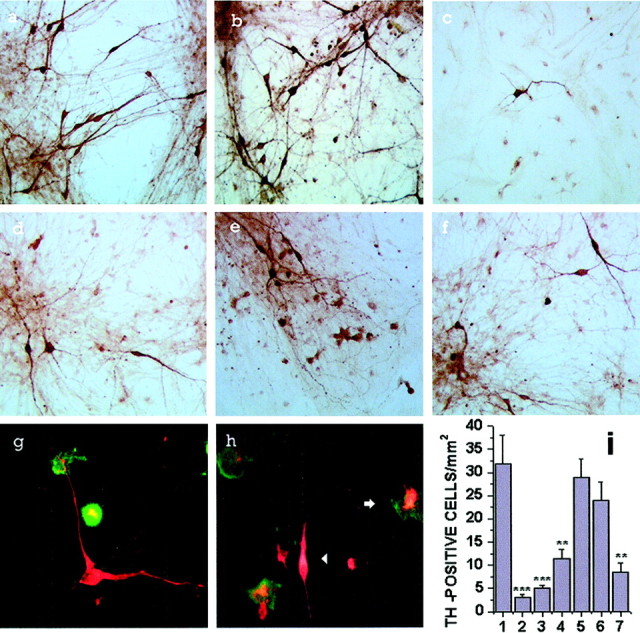
Reactive microglia-induced primary mesencephalic cell injury. Representative photographs of TH immunostaining in primary mesencephalic cell cultures (a) or cocultures with microglia (b–f) in addition of vehicle (b), LPS (4 μg/ml) (c), high-dose PD IgG (200 μg/ml) (d), high-dose DA-Q-M membranes (150 μg/ml) (e), and low-dose PD IgG (20 μg/ml) + low-dose DA-Q-M membranes (15 μg/ml) (f) for 2 d. Double staining of TH-positive neurons (red) and OX-42-positive microglia (green) in the vehicle-treated cocultures (g) and PD IgG-activated cocultures (h). Inh, note a reactive microglia surrounding and phagocytosing an injured dopaminergic neuron (arrow), and a TH-positive neuron with attenuated neurite and shortened cell body (arrowhead). I, Quantitative counting of TH-positive cells in cocultures. Control cocultures of primary mesencephalic cells with microglia treated with vehicle (column 1), 4 μg/ml LPS (column 2), high-dose PD IgG (200 μg/ml) (column 3), high-dose DA-Q-M membranes (150 μg/ml) (column 4), low-dose DA-Q-M membranes (15 μg/ml) (column 5), low-dose PD IgG (20 μg/ml) (column 6), and low-dose PD IgG + low-dose DA-Q-M membranes (column 7). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001 versus control cocultures (column 1).
