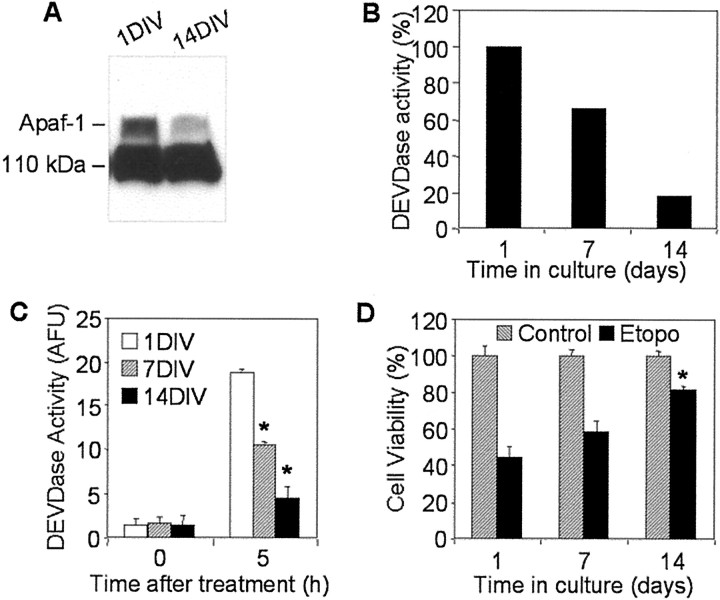
Fig. 4.
Analyses of Apaf-1 expression, cytochromec-inducible apoptotic potential, and cell viability in primary cultures of rat cortical neurons. A, One hundred micrograms of cytosolic proteins from 1 or 14 DIV primary rat cortical neurons were separated in 5% SDS-PAGE followed by staining with an Apaf-1 antibody (Chemicon). B, Protein extracts from 1, 7, or 14 DIV primary rat cortical neurons were incubated in the presence of cytochrome c and dATP as described in Materials and Methods. Caspase-3-like activity was assayed fluorometrically by measuring the accumulation of free AMC resulting after cleavage of Ac-DEVD-AMC. Data are expressed as percentage of 1 DIV-induced caspase activity. C, One, 7, or 14 DIV primary rat cortical neurons were treated with 50 μmetoposide for 5 hr. Control cultures (0 hr) served as negative controls. Caspase-3-like activity in cytosolic extracts from treated or control cells was assayed fluorometrically. Protease activity is expressed in arbitrary fluorescence units ± SD (n = 6). *p < 0.001, compared with caspase-3 activity in etoposide-treated 1DIV cells, by ANOVA, followed by Dunnett's test. D, One, 7, or 14 DIV primary neurons were treated with 50 μm etoposide (Etopo) for 24 hr, and cell viability was analyzed by measurement of calcein AM fluorescence. Data are expressed as a percentage of the value for control cells not exposed to etoposide ± SD (n = 6). *p < 0.001, compared with viability of 1DIV cells after 24 hr etoposide treatment, by ANOVA, followed by Dunnett's test.