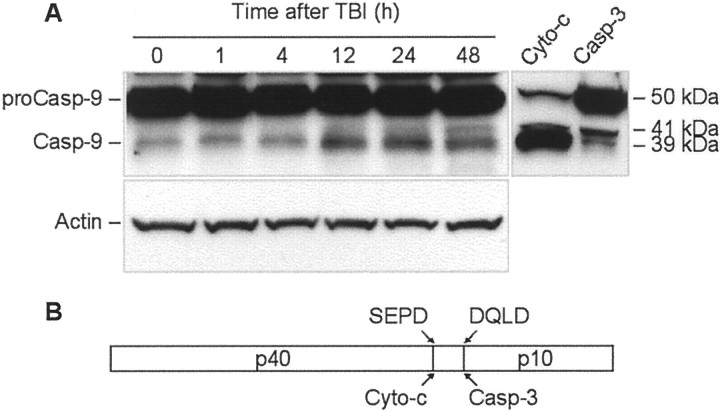
Fig. 7.
TBI induces time-dependent cleavage of procaspase-9 in rat brain cortex. A, Eighty microgram aliquots of cytosolic protein extracts isolated from sham control or traumatized rat cortex at indicated times after TBI were subjected to 10% SDS-PAGE and transferred to a nitrocellulose filter. As a positive control for cleavage specificity, 80 μg aliquots of protein extracts from 2-d-old rat cortex were preincubated in the presence of either recombinant active rat caspase-3 (Casp-3; 20 U; Alexis) or cytochrome c (Cyto-c) and dATP for 1 hr at 37°C. The filter was probed with a monoclonal antibody against caspase-9 (Casp-9; clone 5B4; MBL). The antigen–antibody complexes were visualized by an ECL method as described in Materials and Methods. To control protein loading, membranes were stripped and reprobed with an antibody against β-actin. B, Schematic diagram illustrating processing of procaspase-9. Procaspase-9 is processed preferentially at the SEPD site within the apoptosome and at the DQLD site by caspase-3 to generate the large subunit (p40) and small subunit (p10) of mature caspase-9.