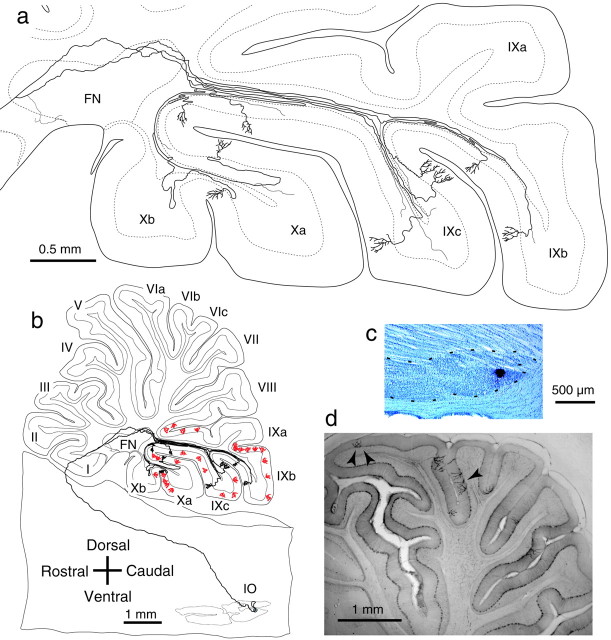
Fig. 1.
Projection patterns of single olivary axons in the cerebellum. a, Intracerebellar trajectory of a single olivocerebellar axon labeled after a small injection of biotinylated dextran amine (BDA) into the mediocaudal portion of the MAO (reconstructed from 77 serial parasagittal sections). This axon gave rise to nine climbing fibers terminating in uvula (lobule IXb–c) and nodule (lobule Xa), and thin collaterals terminating in the cerebellar nucleus and the granular layer. b, Entire trajectory of the same axon shown in a with all the other climbing fibers (n = 28, red) labeled by the tracer injection. All climbing fibers were distributed from caudal lobule VIII to lobule X. c, Photomicrograph of the injection site in the inferior olive shown in b.d, Photomicrograph of labeled climbing fibers in a parasagittal section. Arrowheads indicate the three labeled climbing fibers belonging to a single inferior olive neuron. Digital focusing and enhancement were used. Abbreviations in this and subsequent figures and legends: I–X, lobules I–X;a–d, sublobules a–d; CP, copula pyramidis; Cr I, crus I ansiform lobule; Cr II, crus II ansiform lobule; DN, dentate nucleus; DPFL, dorsal paraflocculus; FL, flocculus; FN, fastigial nucleus; IN, interposed nucleus; IO, inferior olive;MAO, medial accessory olive; Par, paramedian lobule; PO–DL, dorsal lamella of the principal olive; Sim, simple lobule;VPFL, ventral paraflocculus.