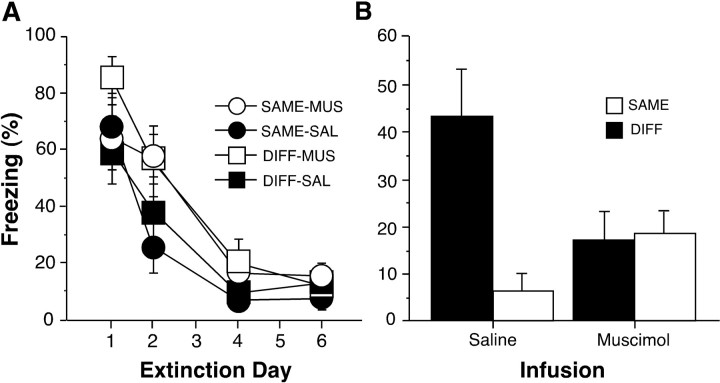
Fig. 4.
Muscimol infusion into the dorsal hippocampus disrupts the context-specific expression of extinction (experiment 2).A, Extinction to the CS. Mean ± SEM percentage of freezing for the first five CS presentations across the 6 d of extinction in contexts B and C. Extinction commenced 1 d after fear conditioning and was conducted in one of two contexts (context B or C) that were different from the conditioning context (context A). The group labels refer to the treatment conditions imposed during retrieval testing (not during extinction training). This permits an assessment of the extinction performance of each group before the retrieval test. Hence, MUS and SAL refer to infusions that were to be given before retrieval testing (no infusions were made during extinction training). Retrieval testing after extinction training was conducted either in the same context as extinction (SAME) or in a context in which the rats did not receive CS-alone presentations (DIFF). Data were not collected on days 3 and 5 of extinction because of a technical problem. B, Mean ± SEM percentage of freezing during the first minute after CS onset. Rats were tested either in the same context in which extinction took place (SAME,open bars) or in a context in which no CS-alone presentations were given during the extinction phase of training (DIFF,filled bars). Retrieval testing took place 20–25 min after an intrahippocampal infusion of either muscimol or saline.