Fig. 4.
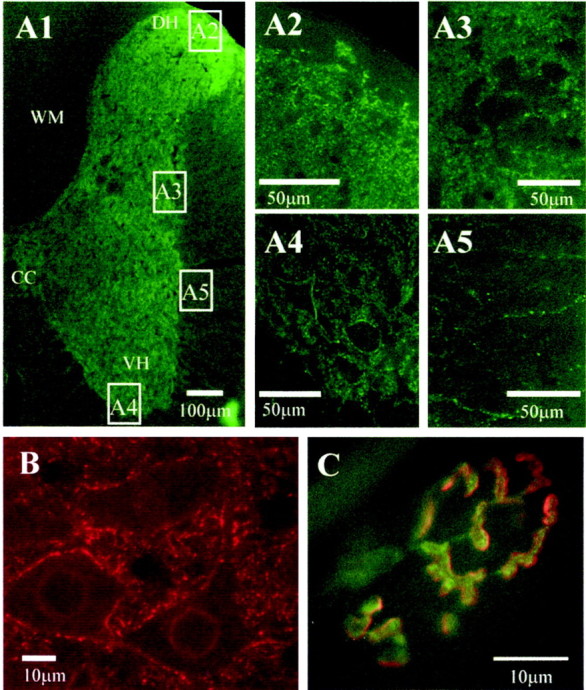
Widespread P2X7 receptor immunoreactivity in the spinal cord, medulla oblongata, and at the neuromuscular junction is localized to punctate structures.A1, Half section of the spinal cord stained for P2X7 immunoreactivity and detected with Alexa488 (green). Labeling is dense in the neuropil of the spinal cord, but less so in the white matter. CC, Central canal; VH, central horn; DH, dorsal horn; WM, white matter. Areas indicated in boxes are illustrated at higher magnification as appropriate. Dense fiber staining is evident in the dorsal horn (A2), intermediolateral cell column (A3), and the ventral horn, where labeled structures appear to surround the somatic membrane of large motoneurons (A4). In the white matter (A5), occasional labeled fibers can be observed. B,P2X7 immunoreactivity is also ubiquitous throughout the medulla oblongata. In this high-magnification view, P2X7immunoreactivity (detected with Cy3, red) is observed in punctate structures in the neuropil as well as surrounding the somatic membrane of neurons in the hypoglossal nucleus. C,Mammalian motor nerve terminals are also immunoreactive for P2X7 receptors. Transversus abdominis muscle from adult mice contained P2X7 receptor immunoreactivity localized to the motor nerve terminal (green, detected with FITC), which appear to be distinct from the postsynaptic receptors (red, labeled withTRITC-α-bungarotoxin).
