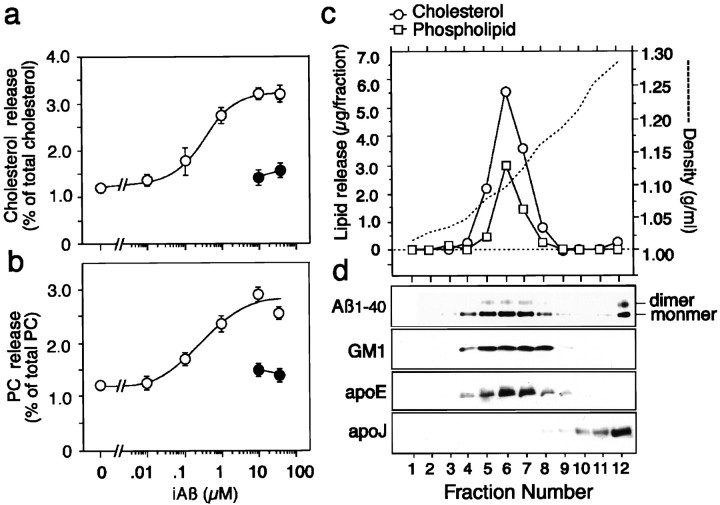
Fig. 4.
iAβ promotes lipid release from astrocytes in culture. Astrocyte-rich cultures were labeled with [14C]acetate for 48 hr as described in Materials and Methods. Cells were then washed three times with DMEM and incubated with iAβ1–40 or fresh Aβ at various concentrations for 4 hr. The conditioned media were collected and then filtered. The lipids that were released into the medium and the intracellular lipids were extracted and analyzed as described in Materials and Methods. iAβ (○) promoted the release of cholesterol (a) and phosphatidylcholine (PC) (b) in a dose-dependent manner; fresh Aβ (●) did not. Data are mean ± SE for four samples. The scale bars are smaller than the symbol size at 0 μm (a and b). Density gradient ultracentrifugation analysis was performed with the conditioned medium of astrocytes in the presence of iAβ. Astrocytes plated in six-well plastic plates were incubated with Aβ1–40 (10 μm) in DMEM for 24 hr. The culture medium was collected, filtered through a 0.45 μm filter, and subjected to an initial discontinuous density gradient prepared using KBr solution as described in Materials and Methods. After ultracentrifugation, the solution was fractionated. The density and cholesterol and phospholipid content in each fraction were determined (c). Aliquots of 10 μl from each fraction were mixed with the same volume of SDS buffer, subjected to SDS gel electrophoresis, and immunoblotted with antibodies against Aβ (BA27), apoE (AB947), and apoJ. GM1 ganglioside in each fraction was detected with HRP-conjugated chorea toxin-B (d).