Fig. 7.
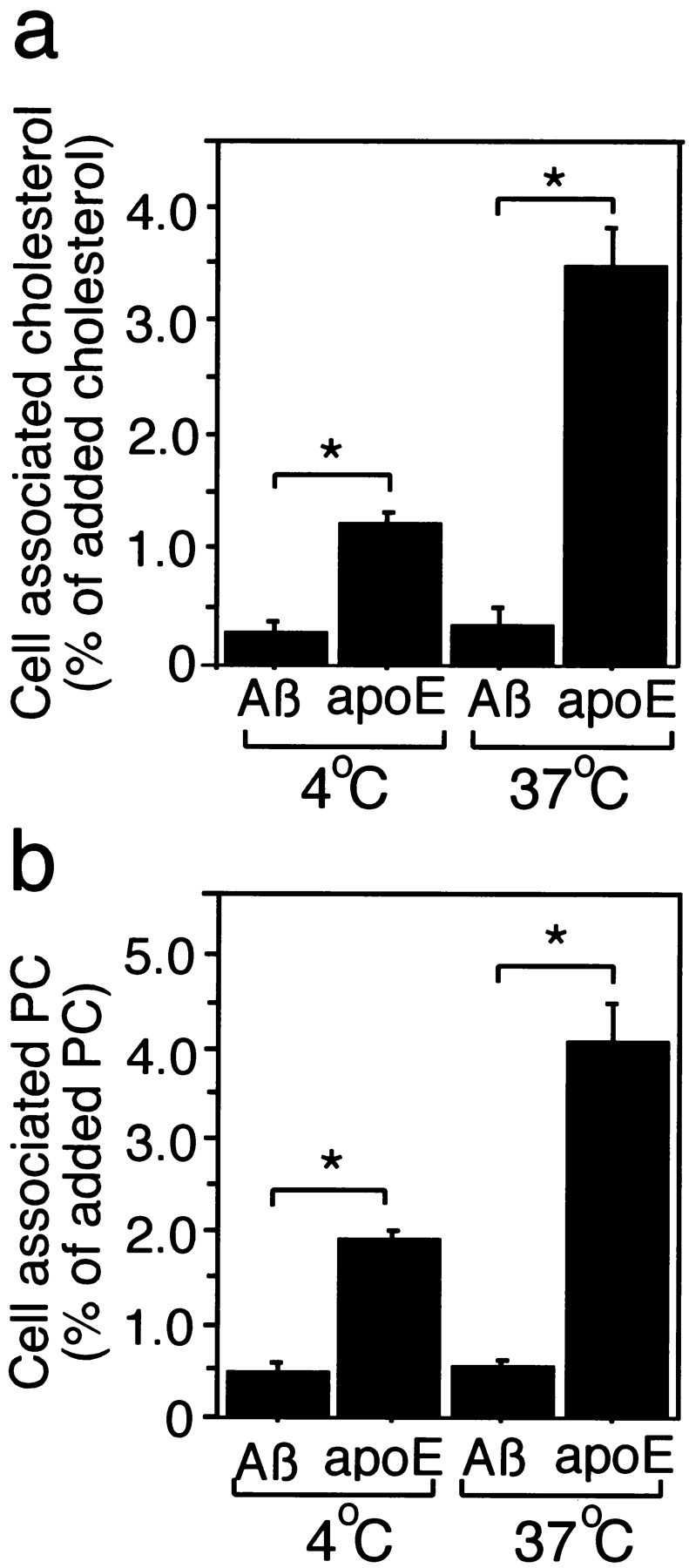
Binding affinity and internalized efficacy of Aβ-lipid particles into neurons. Astrocyte-rich cultures were labeled with [14C]acetate for 48 hr as described in Materials and Methods. Cells were then washed three times with DMEM and incubated with 10 μm iAβ 1–40 or 0.25 μmhuman recombinant apoE3 for 24 hr. The conditioned media were obtained, filtered using a 0.45 μm filter, and subjected to density-gradient ultracentrifugation at 34,000 rpm for 48 hr in a Beckman SW 41-Ti rotor. The HDL fractions were then collected and dialyzed. The radioactivity in each sample was determined by a scintillation counter and normalized with DMEM. The normalized conditioned medium containing iAβ or apoE was added to neuronal cultures at 4 or 37°C. Twenty minutes after the addition, the cultures were washed three times with cold PBS and dried under air flow at room temperature. The lipids in each culture were extracted by incubation with hexane/isopropanol (3:2 v/v) solution for 1 hr. Then the solution was moved into tubes and dried under N2 gas. The extracted lipids were then dissolved in chloroform, developed in HPTLC, and quantified by BAS2500 (Fuji Film, Tokyo, Japan). a, The ratio of the labeled cholesterol associated with neurons was significantly lower at both 4 and 37°C in the cultures incubated with conditioned medium treated with iAβ1–40. However, it was significantly higher at both 4 and 37°C in the cultures incubated with apoE. Similar results were observed for the ratio of the labeled phosphatidylcholine in association with the cells (b). Data are mean ± SE for six samples. *p < 0.003.
