Fig. 16.
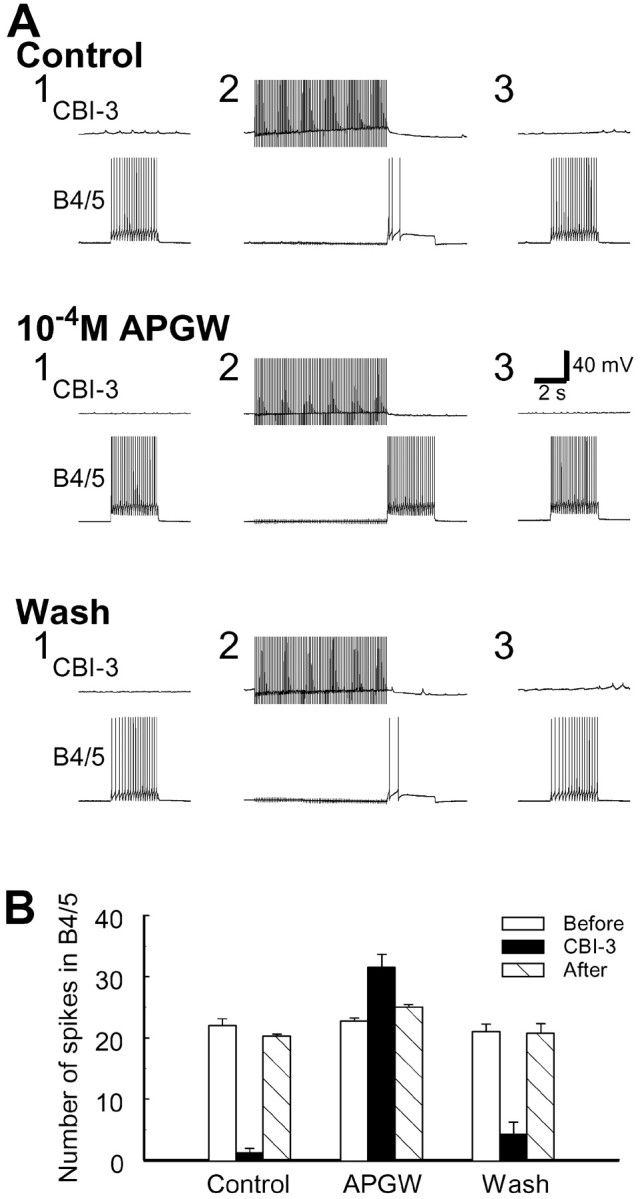
APGWamide occludes the CBI-3-induced inhibition of B4/5 excitability. A, Test pulses in B4/5 (3 sec duration) were applied every 30 sec to induce regular firing in B4/5. CBI-3 was stimulated by brief current pulses at 10 Hz for 8 sec before injection of current pulses into B4/5. Both in control conditions and after APGWamide washout, CBI-3 suppressed B4/5 spiking (compare Fig.14B). However, in the presence of 10−4m APGWamide, CBI-3 no longer suppressed B4/5 spiking. In fact, B4/5 activity was increased. Note that APGWamide by itself also reduced B4/5 excitability (Fig.15B). The size of current pulses injected into B4/5 during bath application of APGWamide was increased to induce B4/5 firing comparable with that in control. B, Plot of group data of the effect of APGWamide on CBI-3 inhibition of B4/5 excitability (n = 4). Error bars indicate SEM.
