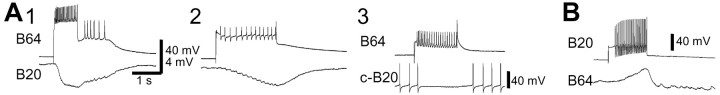
Fig. 7.
Synaptic connections of B20 with the retraction phase interneuron B64. A, B64 elicited IPSPs in B20 in normal saline (1). These IPSPs persisted in high-divalent saline (2). The IPSPs in B20 followed B64 presynaptic spikes one-for-one. A, 3, Inhibitory connections from B64 were functional, because B64 suppressed the firing of c-B20 in normal saline. B20 is not spontaneously active; therefore, we elicited spiking in B20 by a constant intracellular current injection. B, Neuron B20 elicited a mixed response (early excitation followed by slow inhibition) in B64 in normal saline. This response is probably polysynaptic, because it was not present in high-divalent saline (data not shown).