Fig. 1.
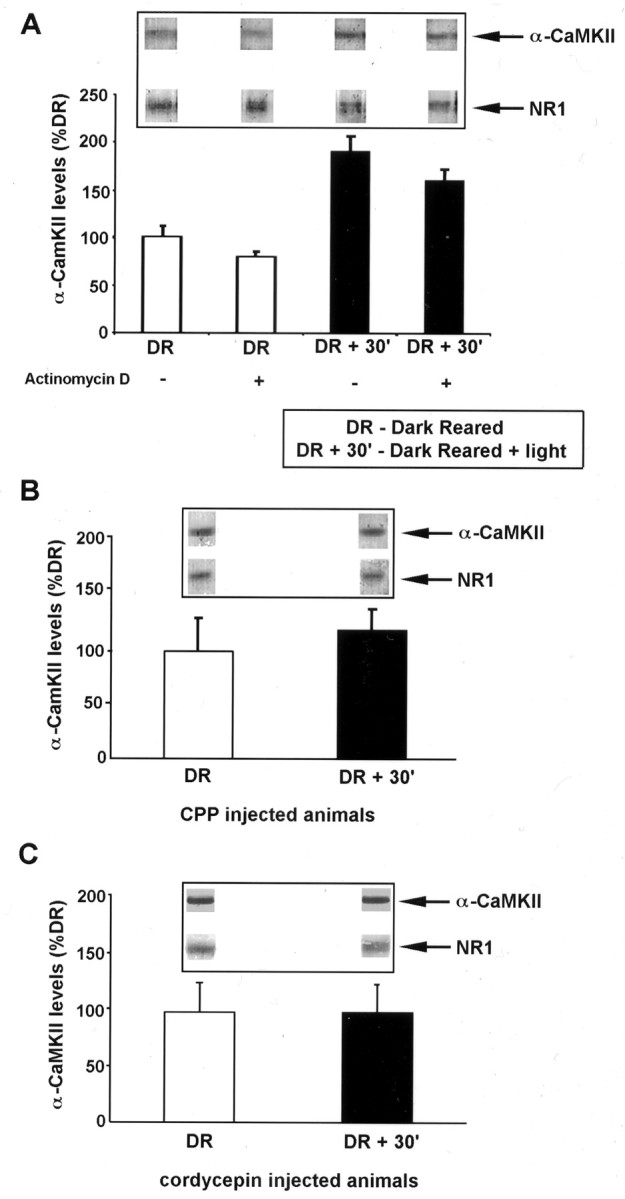
Experience-induced increase in α-CaMKII protein in the visual cortex mediated by NMDAR activation and mRNA polyadenylation. A, Quantification of α-CaMKII levels in synaptoneurosome (SN) fractions isolated from the visual cortex of animals reared in complete darkness (DR) and animals reared in the dark and exposed to light for 30 min (DR + 30′). Western blots for α-CaMKII and NMDAR subunit NR1 were performed from PAGE loaded with equal total protein of SN samples isolated from DR and DR + 30′ visual cortex. Quantitative densitometry was performed on the α-CaMKII bands, and these were normalized to the level of NR1 in the same lane [the amount of NR1 subunit in SN fraction does not change with visual experience (Quinlan et al., 1999)]. Where indicated, actinomycin D (1 mg/kg) was injected (intraperitoneally) 30 min before light exposure. This dose of actinomycin D is effective in blocking protein synthesis in the brain (Jackson, 1972; Pickering and Fink, 1976). Each experiment consisted of two to four rats per treatment group, and results shown are the mean ± SEM of three experiments. Insets show representative bands from one experiment. B, Quantification of α-CaMKII expression as in A, in animals injected with the NMDAR antagonist CPP (10 mg/kg) 30 min before light exposure. Each experiment consisted of two to four rats per treatment group, and results shown are the mean ± SEM of three experiments. C, Quantification of α-CaMKII performed as in A, in animals injected with cordycepin (6 mg/kg) 30 min before light exposure. Each experiment consisted of two to four rats per treatment group, and results shown are the mean ± SEM of three experiments.
