Fig. 2.
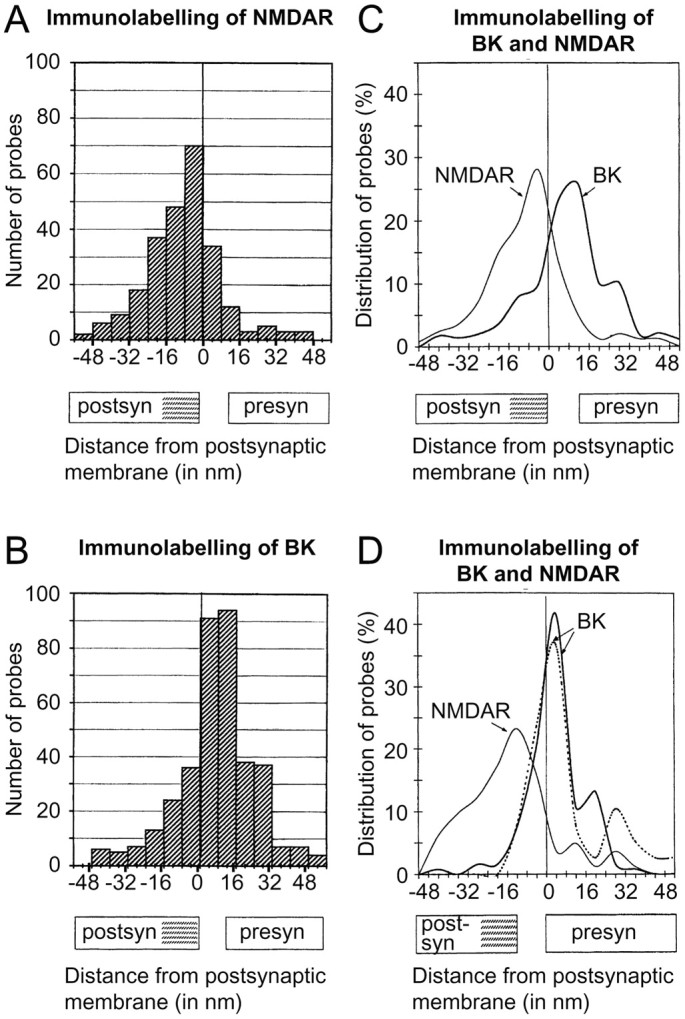
Quantitative analysis of gold particle distributions signaling BK channels (B–D) and NMDA receptors (A, C, D). The particle distribution was assessed along an axis perpendicular to the synaptic specialization (A–D) or extrasynaptic plasma membrane (D, dashed line). The approximate extent of the synaptic cleft and postsynaptic density (hatched) is indicated along theabscissa. Zero is defined as the outer margin of the postsynaptic (A–C) or presynaptic (D) membrane, and gold particles located postsynaptic to the reference line are assigned negative values. Compared with the gold particles signaling NMDA receptors (A), those signaling BK channels (B) are shifted in the presynaptic direction. This is evident in C, where the histograms inA and B have been transformed into curves. The number of gold particles is expressed in percentage to facilitate comparison between the two distributions. The peaks are located at −5 and +12 nm, i.e., over the postsynaptic and presynaptic membranes, respectively. The means were −8.52 ± 1.0 (n = 251) and 7.6 ± 0.9 (n = 366; p < 0.0001), and the kurtosis values were 1.29 and 1.19. D, Distribution of gold particles perpendicular to the presynaptic active zone (solid curves) and perpendicular to extrasynaptic parts of the presynaptic membrane (dashed curve). The analysis was performed exactly as in A–C except for the choice of reference line (outer margin of presynaptic rather than postsynaptic membrane). The BK immunogold distribution does not differ significantly between synaptic and extrasynaptic membrane domains (peaks 4.0 and 3.9 nm; 25 percentiles −1.4 and −1.1 nm). The linear density of gold particles in synaptic and extrasynaptic membranes was 7.0 and 0.26 particles per micrometer, respectively (measured along 41 and 256 μm; 144 synapses). No particles were observed along astrocyte plasma membranes (total length of sample 30 μm). Note that the variance in NMDA receptor immunogold distribution is larger in D than in C (506.6 vs 267.0), whereas the opposite is true for the BK signal (143.8 vs 295.8). This reflects the variability in the width of the synaptic cleft. Because the synaptic membranes are curved, the epitopes accessible for immunogold labeling will show a small shift in the postsynaptic direction relative to the reference line (hatched). Gold particles are indicated.
