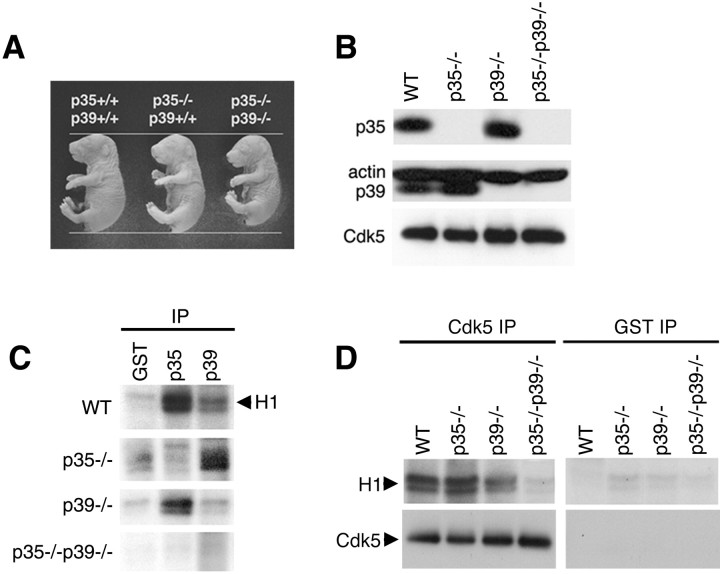
Fig. 2.
Absence of Cdk5-associated kinase activity in p35–/–p39–/– double-null brains. A, p35–/–p39–/– double-mutant mice isolated at E18.5 are consistently smaller than are wild-type and single-mutant littermates. B, Absence of both p35 and p39 protein in p35–/–p39–/–mice is shown. Western blot analysis of whole-brain lysates from wild-type, p35–/–, p39–/–, and p35–/–p39–/– P0 pups is shown. p39 is upregulated in the absence of p35, but p35 protein is unaffected by the loss of p39. C, p35–/–p39–/– mice show absence of p35- and p39-associated kinase activity, whereas single-mutant mice display residual kinase activity. Five hundred micrograms of brain lysates of wild-type, p35–/–, and p39–/– P0 pups were immunoprecipitated with polyclonal p35 and p39 antibodies and a polyclonal GST antibody as negative control and assayed for histone H1 kinase activity. p35–/– brain lysates exhibit histone phosphorylation when immunoprecipitated with p39 antibody; p39–/– brain lysates exhibit histone phosphorylation when immunoprecipitated with p35 antibody.D, Absence of Cdk5-associated kinase activity in p35–/–p39–/– mice is shown. Both p35–/– and p39–/– brain lysates continue to display Cdk5-associated kinase activity, whereas kinase activity is absent or equivalent to background (GST-immunoprecipitated) levels in p35–/–p39–/– brain lysates.WT, Wild type.