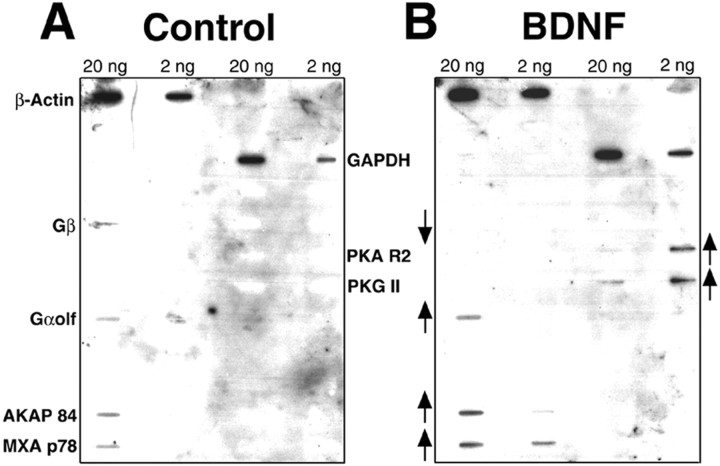
Fig. 4.
Slot blot analysis reveals BDNF-induced changes of G-protein family genes. RNA derived from control (A) or BDNF-treated (B) hippocampal cultures was used to prepare radioactively labeled cDNA. The cDNA was hybridized to a blot containing clones of G-protein-related genes at 2 or 20 ng of DNA. The expression of several genes increased in the BDNF-treated samples (↑). AKAP 84, Anchor protein for regulatory subunit of protein kinase A;Gαolf, protein involved in transduction of olfactory signals including the GC pathway; MXA p78, interferon-induced protein with GTPase activity; PKA R2, regulatory subunit of protein kinase A; and PKG II, protein kinase G II. The expression of one gene decreased in the BDNF-treated sample (↓): Gβ, the β subunit of the G-protein. Two housekeeping genes did not show differential expression:β-actin and GAPDH, glyceraldehyde phosphate dehydrogenase.