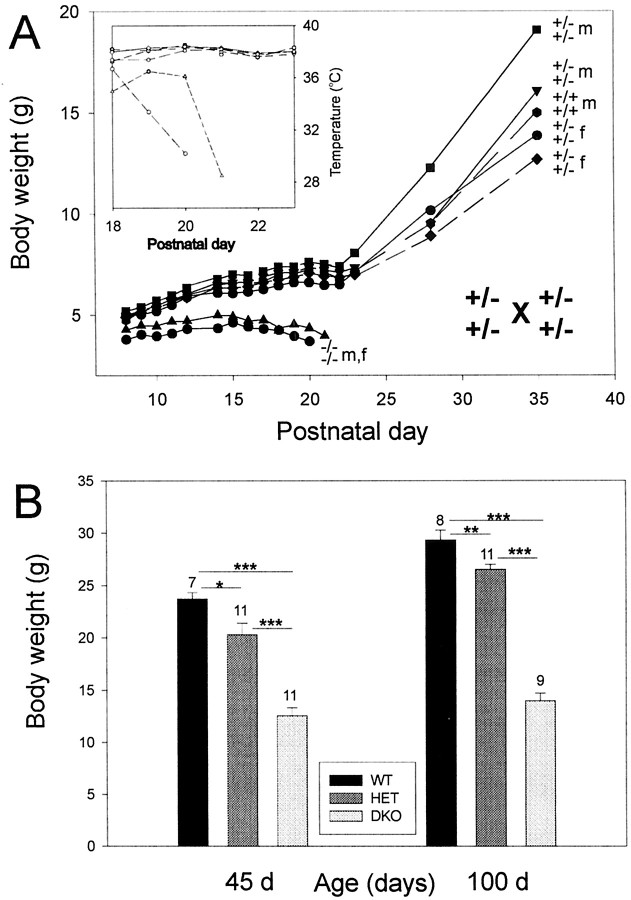
Fig. 2.
A, Kv3.1 and Kv3.3 K+ channels are required for postnatal development. In this litter of seven pups, two double mutants began to loose weight at ∼P15 and died by P20 and P21. Wild-type and heterozygous littermates gained weight normally and grew to adulthood.Inset, The drop in body temperature of the double mutants is shown. The Kv3.1 and Kv3.3 genotypes and the gender [female (f), male (m)] are shown on the right. B, Adult Kv3.1/Kv3.3-deficient mice are smaller than are wild-type and double-heterozygous mice. At 1.5 months (45 d) and 3.5 months (100 d) of age, Kv3.1−/−Kv3.3−/−(DKO), Kv3.1+/−Kv3.3+/−(HET), and Kv3.1+/+Kv3.3+/+(WT) male mice differ from each other in body weight [mean ± SEM and number of mice (above eachvertical bar) shown; one-factor ANOVA; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001].