Fig. 9.
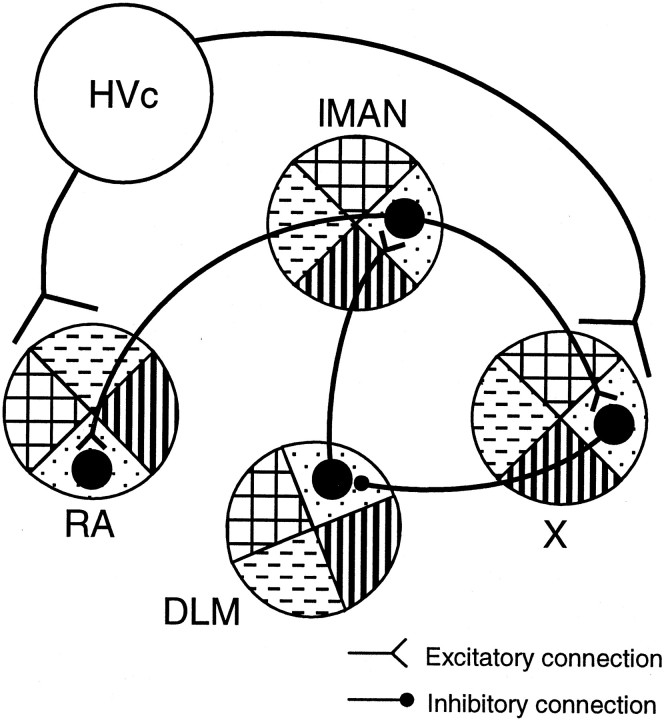
Summary of the major results from this study. In the sagittal plane, area X projects topographically to DLM, with the terminals in DLM rotated ∼70° ccw from their injection site (rotation of filled patterns in different areas of the nuclei). The DLM → lMAN projection is also topographic, with the target of the projection in lMAN rotated ∼70° cw from the source of the projection in DLM. Topographic mapping in the sagittal plane for the lMAN → area X projection was also confirmed and found to involve little if any rotation in the sagittal plane. The spatial relationships among the three AFP nuclei suggest that corresponding areas within each nucleus are interconnected. The AFP is thus topographic throughout its projections and forms a closed loop. With the topographic output to RA, which is myotopically organized, each portion of the loop may represent a functional unit related to learning to activate a subset of muscles for vocal production.