Fig. 1.
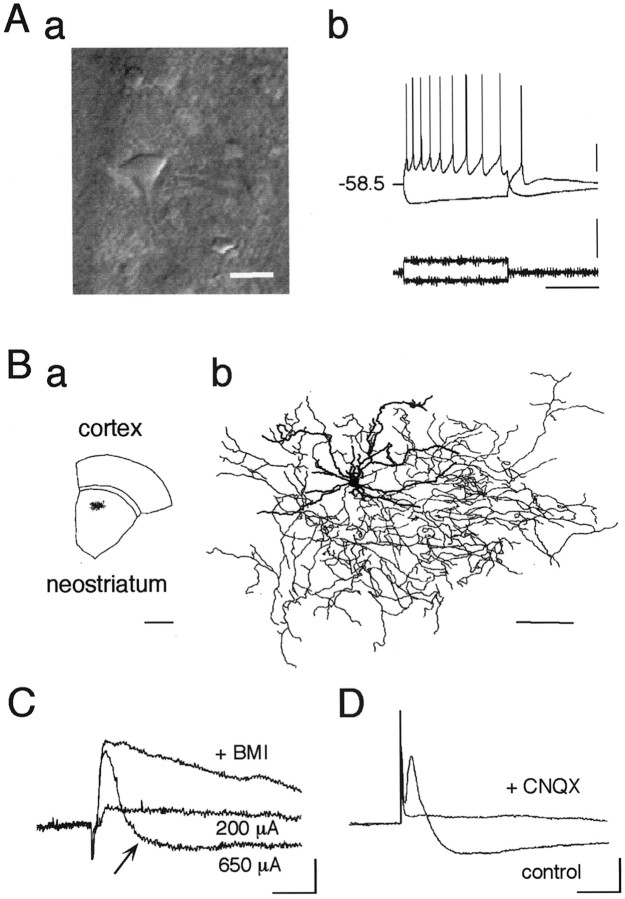
Cortico/thalamostriatal stimulation evokes EPSP as well as disynaptic IPSP in the striatal cholinergic interneurons.Aa, IR-DIC video image of a cholinergic interneuron just before recording. This neuronal type is exceptionally large compared with other types of neurons. Average diameter: long, 19.5 μm; short, 13.5 μm (n = 32). Scale bar, 20 μm.Ab, Current-clamp recordings from a cholinergic interneuron shown in Aa during injection of depolarizing and hyperpolarizing current pulses. Resting membrane potential was −58.5 mV. Calibration: vertical bar, 20 mV (top), 500 pA (bottom); horizontal bar, 500 msec. Ba, Slice containing a large aspiny neuron, which was stained with biocytin during whole-cell recording and reconstructed in Bb.Bb, Dendrites (thick lines) and axons (thin lines) are superposed. Large aspiny cells had fewer spiny dendrites than medium spiny cells (data not shown). Note the wide distributions of both dendrites and axons. Scale bars:a, 1 mm; b, 100 μm. C, Postsynaptic potentials evoked by electrical stimulation (amplitude, 200 and 650 μA; duration, 400 μsec) of white matter. Note that a stimulus of larger amplitude (650 μA) evoked a hyperpolarizing component after EPSP that was abolished by bath application of BMI (30 μm; +BMI). D, Both components were completely abolished by CNQX (10 μm;+CNQX). Calibration (C,D): 2 mV, 20 msec.