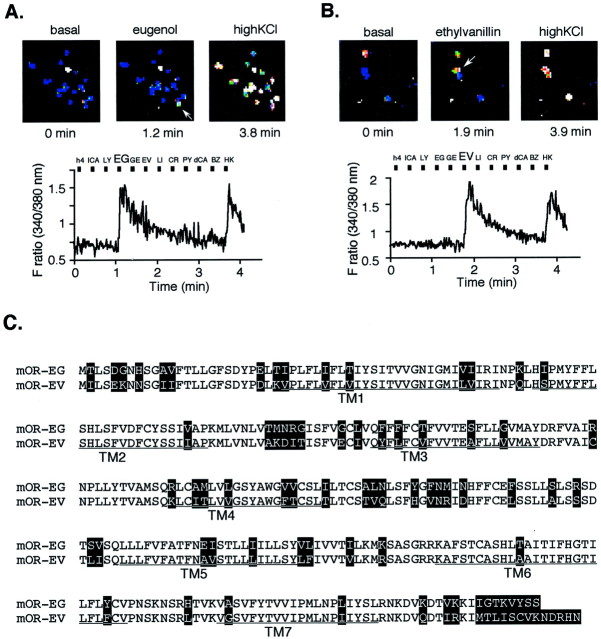
Fig. 1.
Functional cloning of an olfactory receptor gene expressed in single olfactory neurons that responded to EG or EV. A, The Ca2+ response of a single olfactory neuron to EG (shown by an arrow in the top middle panel) in reflected changes in fura-2 fluorescence intensity ratios (340/380 nm). The odorants were applied to olfactory neurons for 4 sec during the times indicated by the black boxes. The cells were washed for 20 sec continuously between odorant applications. Names of odorants are abbreviated as follows: h4, 1-butanol;lCA, l-carvone; LY, lyral;EG, eugenol; GE, geraniol;EV, ethyl vanillin; LI, lilial;CR, cresol; PY, pyridine;dCA, d-carvone; and BZ, benzene (each 1 mm). HK stands for high KCl buffer. Pseudocolored images of Ca2+ measurements were taken at three representative time points (top panel). White cells indicate high intracellular Ca2+ levels, and blue cells represent the basal level and outlines the shape of each cell. B, The Ca2+ response of a single olfactory neuron to EV. C, The predicted amino acid sequences of the olfactory receptor genes that were isolated from single olfactory neurons depicted in A and B, which correspond to mOR-EG and mOR-EV, respectively. The putative TMs areunderlined. In the alignment of the mOR-EG and mOR-EV, residues that differ are highlighted.