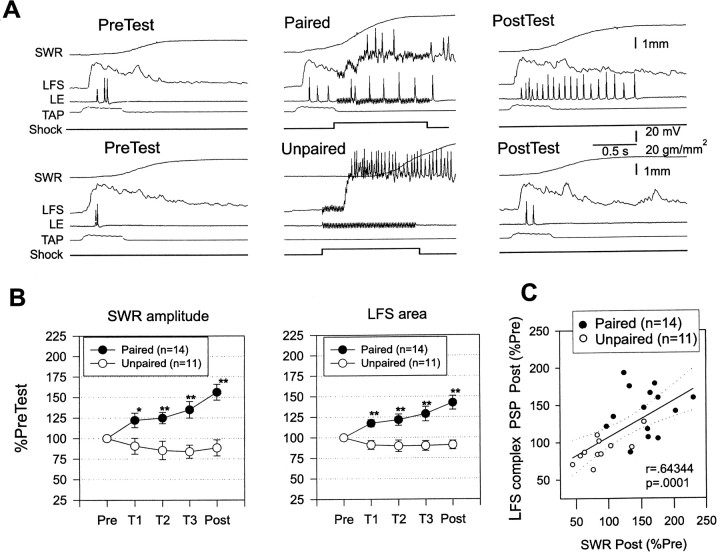
Fig. 5.
Facilitation of the complex PSP in LFS motor neurons during classical conditioning. A, Examples of the complex PSP produced in an LFS motor neuron by the siphon tap on the pretest and the final post-test after paired and unpaired training. In these experiments, the motor neuron was hyperpolarized to approximately −90 mV for a few seconds to prevent it from firing during the tap. B, Average magnitudes of siphon withdrawal and the complex PSP recorded in the same experiments. Paired training produced a greater increase in the amplitude of siphon withdrawal that was accompanied by a greater increase in the area of the complex PSP in the first 1 sec after its onset. The average values on the pretest were 1.8 mm (paired) and 1.7 mm (unpaired) for siphon withdrawal, and 36,369 mVmsec (paired) and 34,516 mVmsec (unpaired) for PSP area, not significantly different by t tests. The average unconditioned responses to the first tail shock were 3.7 mm (paired) and 4.1 mm (unpaired), not significantly different.C, There was a significant correlation between the increase in the amplitude of siphon withdrawal and the increase in the area of the complex PSP.