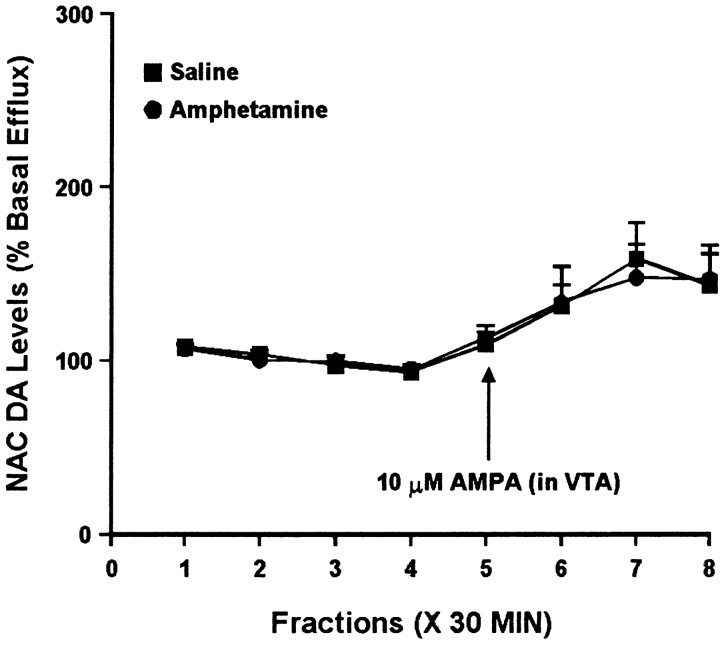
Fig. 2.
Effect of local administration of 10 μm AMPA into the VTA on DA efflux from the ipsilateral NAC of amphetamine- and saline-pretreated rats tested 10–14 d after the last injection. AMPA was administered locally into the VTA for 30 min during sample 5. One-way ANOVA with time as the repeated measure indicated a significant change in DA efflux over time in both the saline group (F(7,35) = 5.08; p < 0.001) and the amphetamine group (F(7,28) = 4.70; p< 0.01). Contrast analysis indicated significant differences between the weighted means of baseline samples (1–4) and post-AMPA samples (5–8) for both groups (p < 0.001). Two-way ANOVA with time as the repeated measure indicated no significant difference between the amphetamine and saline groups (group × time effect,F(7,63) = 0.11; p = 0.99). Basal DA levels were 34.1 ± 6.2 fmol/sample in the saline group (n = 6) and 37.6 ± 3.6 fmol/sample in the amphetamine group (n = 5) and did not differ significantly between groups.