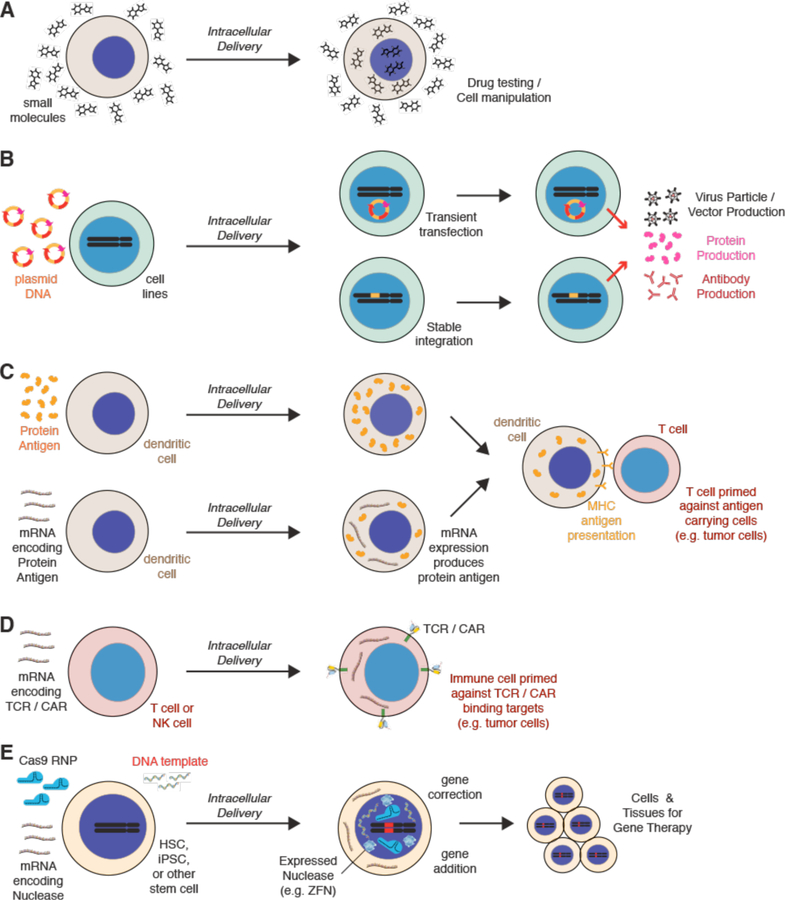
Figure 28.
In vitro and ex vivo applications of intracellular delivery achieved with electroporation. (A) Delivery of impermeable drugs to the intracellular space for drug testing and/or cell manipulation. (B) Transfection with plasmid DNA encoding proteins, antibodies, and viral components for biomanufacturing purposes. (C) Loading of protein antigens or mRNA encoding such into dendritic cells. Presentation of antigen fragments through MHC pathways is able to prime T cells against cells carrying the antigens and may be useful for cancer immunotherapy. (D) Transfection of cytotoxic immune cells with mRNA encoding TCRs and/or CARs can be used to direct immune cells against specific cell targets, such as cancer cells. TCR = T cell receptor. CAR = chimeric antigen receptor. (E) Genome-editing molecules can be delivered into stem cells for purposes of adding, deleting, or correcting genes. Modified stem cells can then be expanded for potential deployment in cell-and tissue-based gene therapy. Red signifies areas of the genome that have been edited. ZFN = zinc finger nuclease.