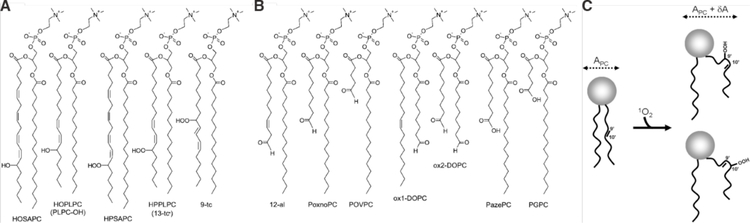
Figure 41.
Chemical structures of oxidized phosphatidylcholines and their effects on bilayer packing. (A) Hydroxy- (HOSAPC and HOPLPC) and hydroperoxy-(HPSAPC, HPPLPC, and 9-tc) phospatidylcholines. Different cis/trans isomers are possible. 13-tc refers to trans-11, cis-9 isomer of HPPLPC. (B) Truncated (cleaved chain) phosphatidylcholines with aldehyde (12-al, PONPC, POVPC, ox1-DOPC, and ox2-DOPC) and carboxylic (PAzPC and PGPC), functional groups. For further details see reference 14671467. (C) Example of conformation changes that lipid molecules undergo due to peroxidation. In this case singlet oxygen adds the more hydrophilic group-OOH at either 9 or 10 position, which migrates to the bilayer surface. This imposes a kink to the acyl chain, with an accompanying increase in area δA per lipid. Figure taken from reference 397397.