Table 4.
Cargo delivery mechanism versus scale of throughput for nano- and micro-mechanical membrane disruption techniques. For injection mechanisms, the nano or micro-mechanical element is hollow, thus allowing injection of cargo. Dissociation-based delivery works by enabling cargo to detach from the penetrating element once inside the cell. For permeabilization, the cargo is in the extracellular solution and flows into the cell by diffusion upon withdrawal of the penetrating element. References for each example are included.
| Injection | Dissociation | Permeabilization | |
|---|---|---|---|
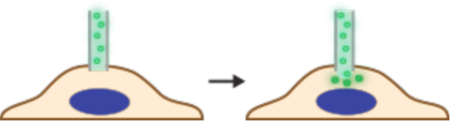 |
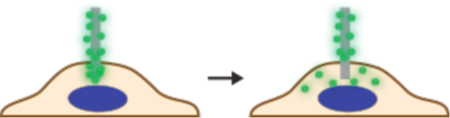 |
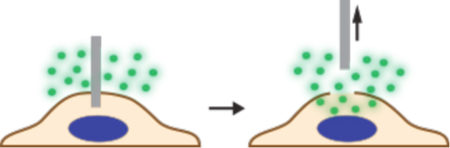 |
|
| Single cell | Microinjection298 Nanoinjection568–571 FluidFM573 |
AFM-controlled CNT tip672 AFM-controlled nanoneedle656–658,673,674 Micromanipulator-controlled metal nanowire675–677 |
CellBee678 Cell Pricking679–682 |
| Parallelized Systems | Nanostraws387,664–666 | Nanowire arrays185,363,634 | Cell Poking654 Microneedle array683 |
