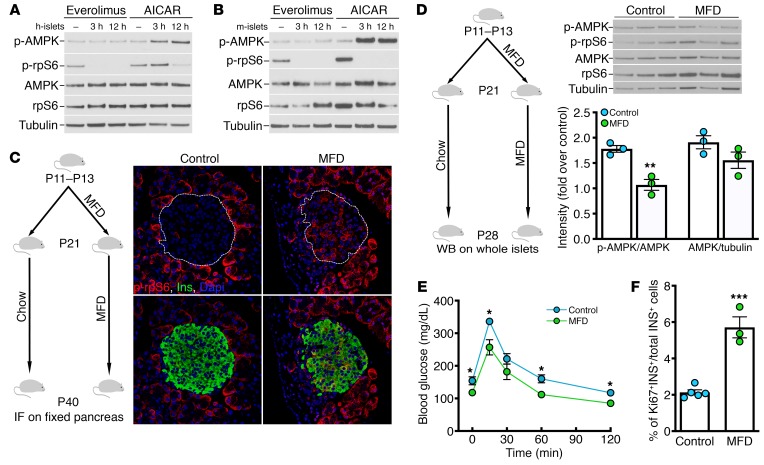
Figure 2. Weaning from maternal milk induces the switch from mTORC1 to AMPK signaling in β cells.
(A and B) Representative immunoblots showing p-AMPK, p-rpS6, total AMPK, total rpS6, and β-tubulin in (A) adult human islets and (B) adult mouse islets after treatment with 1 mM AICAR or 40 μM everolimus for the indicated time (n = 3 for both human and mouse islets except only for the 3-hour AICAR treatment condition, where n = 2). (C) Experimental paradigm for the milk fat–supplemented diet (MFD), and immunofluorescence (IF) staining for insulin (green) and p-rpS6 (red) in representative pancreatic sections from P40 mice otherwise fed either standard chow (control) or the MFD. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue). Original magnification, ×64. (D) Experimental paradigm for the MFD and associated representative Western blots (WB), showing p-AMPK, p-rpS6, total S6, and total AMPK in control and MFD mice. β-Tubulin was used as loading control. Quantification of p-AMPK/AMPK and AMPK/β-tubulin is shown below. **P = 0.0062 (unpaired t test corrected for multiple comparisons using the Holm-Sidak method). (E) Intraperitoneal glucose tolerance test in control and MFD mice (n = 7). *P < 0.05 (unpaired t test corrected for multiple comparisons using the Holm-Sidak method). (F) Percentage of Ki67+ and insulin+ cells in control and MFD islets (n = 3–5). ***P = 0.0002 (2-tailed unpaired t test).