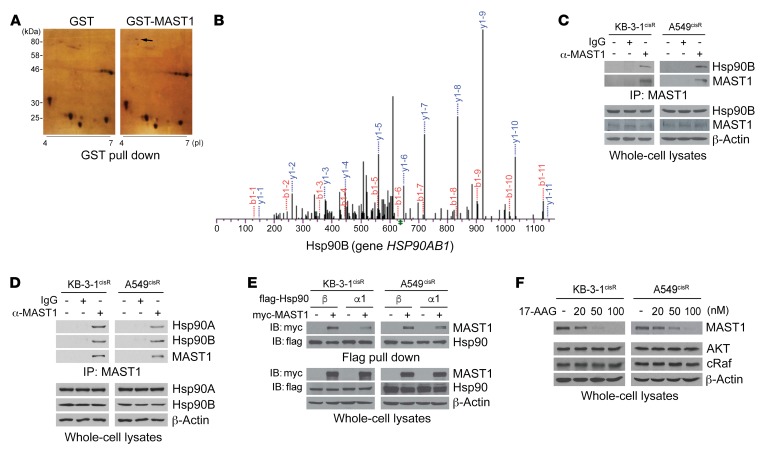
Figure 1. Hsp90B binds to and stabilizes MAST1 in cisplatin-resistant cancer cells.
(A) 2D gel electrophoresis–based proteomic analysis for MAST1-interacting protein identification. 293T cells expressing GST-MAST1 or GST alone were subjected to GST pull down and eluates were separated by 2D gel electrophoresis and visualized by silver staining. Black arrow indicates hsp90B only shown in GST-MAST1 eluates. (B) MS spectra of hsp90B fragment identified by LC-MS/MS. (C) Endogenous interaction between MAST1 and hsp90B was determined by MAST1 coimmunoprecipitation in cisplatin-resistant cancer cells. (D and E) Interaction of hsp90 isoforms with MAST1. Interaction was determined by coimmunoprecipitation. Myc-MAST1 and flag-hsp90B or hsp90A1 were overexpressed in KB-3-1cisR and A549cisR cells in E. (F) Effect of hsp90 inhibition on MAST1 protein level. Cisplatin-resistant cancer cells were treated with increasing concentrations of 17-AAG for 24 hours. MAST1 protein levels were determined by Western blotting. Data are representative of 2 (A and C–E) and 3 (F) independent biological experiments.