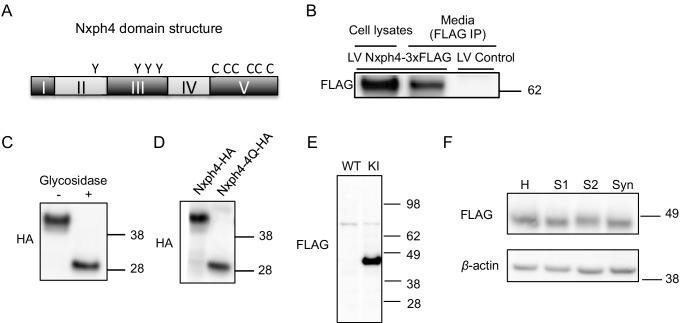
Figure 3. Nxph4 is a glycosylated protein that can be detected in the synaptosomes.
(A) A domain model of Nxph4 (adapted from Missler and Südhof, 1998). I: signal peptide; II: a variable domain; III: a conserved domain; IV: a linker region; V: C-terminal domain. Positions of N-glycosylation sequences are marked by letter Y, and the conserved cysteine residues are identified by the letter C. (B) Immunoblotting of samples from cultured cortical neurons that are infected with lentivirus expressing Nxph4-3xFLAG or the control lentivirus. Nxph4-3xFLAG was detected in the cell lysates as well as the media. (C) Treatment with glycosidase altered the electrophoretic motility of recombinant Nxph4-HA. (D) Nxph4-HA-4Q mutant has a smaller molecular mass compared with the wild type recombinant Nxph4-HA. (E) Immunoblotting analysis detects Nxph4-3xFLAG expression in the KI mouse synaptosomes. (F) Immunoblotting analysis of fractions derived from cerebellar synaptosomal preparation detects Nxph4-3xFLAG in the synaptosomes. β-actin was used as loading control. H: homogenate. S1 and S2 are successive supernatants in the synaptosomal preparation protocol. S2 is also the cytosolic fraction. Syn: synaptosomes.
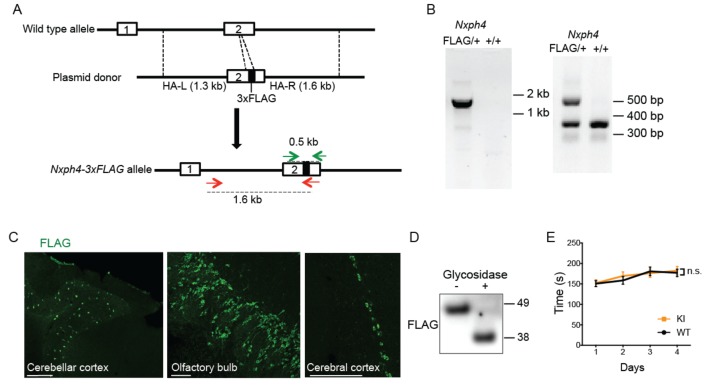
Figure 3—figure supplement 1. Generation and characterization of Nxph4-3xFLAG knock-in mice.
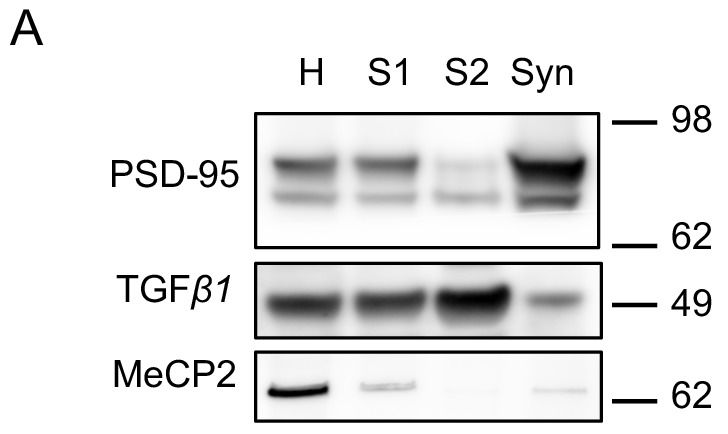
Figure 3—figure supplement 2. Validation of synaptosomes preparation.