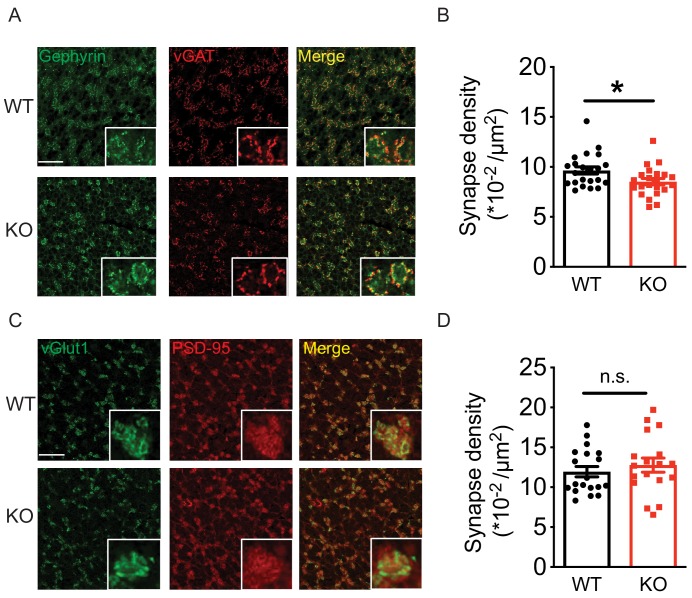
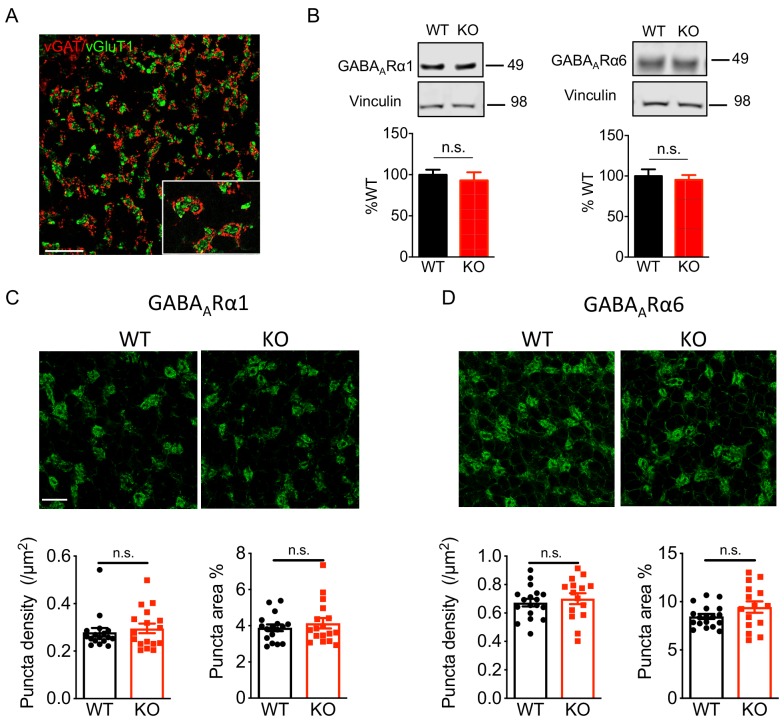
Figure 7. Loss of Nxph4 reduced Golgi-granule inhibitory synapse number.
(A) Gephyrin and vGAT staining in the cerebellar granular layer indicates Golgi-granule inhibitory synapses. (B) Quantification of puncta co-expressing gephyrin and vGAT as an indicator of inhibitory synapse number. (C) vGlut1 and PSD-95 staining in the cerebellar granular layer indicates mossy fiber-granule cell excitatory synapses. (D) Quantification of puncta co-expressing vGlut1 and PSD-95 as an indicator of excitatory synapse number. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. n.s., not significant; *p<0.05; by t test (B) or Mann-Whitney U test (D).