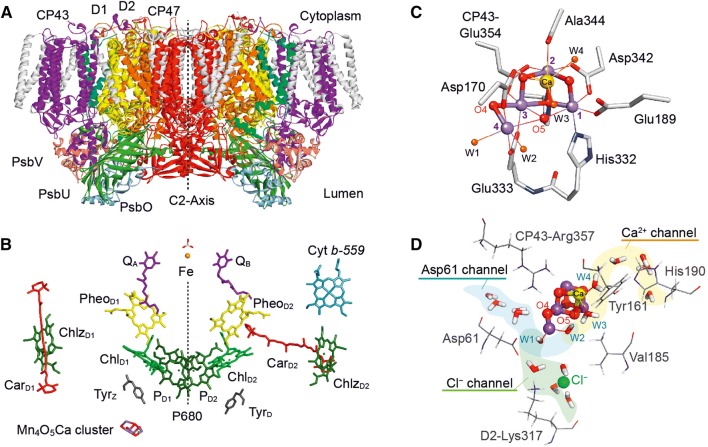
Fig. 2.
X-ray crystallographic structure of photosystem II (PS II) from T. vulcanus. A View of the dimeric protein (molecular weight of the dimer ≈ 700 kDa); the two monomers are related to each other by a C2 axis. The most important subunits are indicated, CP43, CP47, in which the core antenna pigments are located; D1 and D2, which bind all pigments of the reaction center and all cofactors of the electron transport chain, and the small subunits PsbO, PsbU and PsbV, which stabilize the water splitting unit. The D1 protein (yellow) holds the active branch cofactors and the Mn cluster, the D2 protein (orange) the cofactors of the second pigment branch. B Pigment arrangement in one PS II monomer; the two branches are related by a pseudo-C2 axis (dotted line). Shown are the primary donor P680 (four chlorophylls: PD1, PD2, ChlD1, ChlD2), the two pheophytins (PheoD1, PheoD2), the two plastoquinones (QA, QB), and the non-heme iron Fe. Additional chlorophylls (Chlz) and carotenoids (Car), as well as two redox-active tyrosines (TyrZ, TyrD) are also indicated. Next to the active branch (D1) and close to TyrZ/P680, the Mn4O5Ca cluster is located. C Structure of the water oxidizing Mn4O5Ca cluster in PS II with four Mn ions (Mn1 to Mn4, purple) and one Ca (yellow), bridged by oxygen ligands (red). Three Mn ions (1 to 3) and the Ca form a distorted cube bridged by oxygen ligands, the fourth Mn (Mn4) is dangling. Mn4 and the Ca carry two water molecules each (W1 to W4, orange). The coordination of the metal ions by amino acid ligands is also shown; for further details see (Suga et al. 2015; Umena et al. 2011). D Water channels leading to the OEC: Three channels have been localized. Note that also the essential chloride ion is shown in this picture (Suga et al. 2015; Umena et al. 2011). A second Cl− is found farther away from the OEC. It has been pointed out that the channels could be multi-functional